How To Create A GUI In Python Using Tkinter To Display COVID19 Stats
Introduction
In this tutorial, I will guide you through the process of creating a straightforward graphical user interface (GUI) to retrieve COVID-19 related information using Python. This project will help you learn how to use an API and build a GUI application.
Getting Started
Before diving into the code, ensure you have Python installed on your machine. If you need assistance with installation, there are plenty of tutorials available online.
API Information
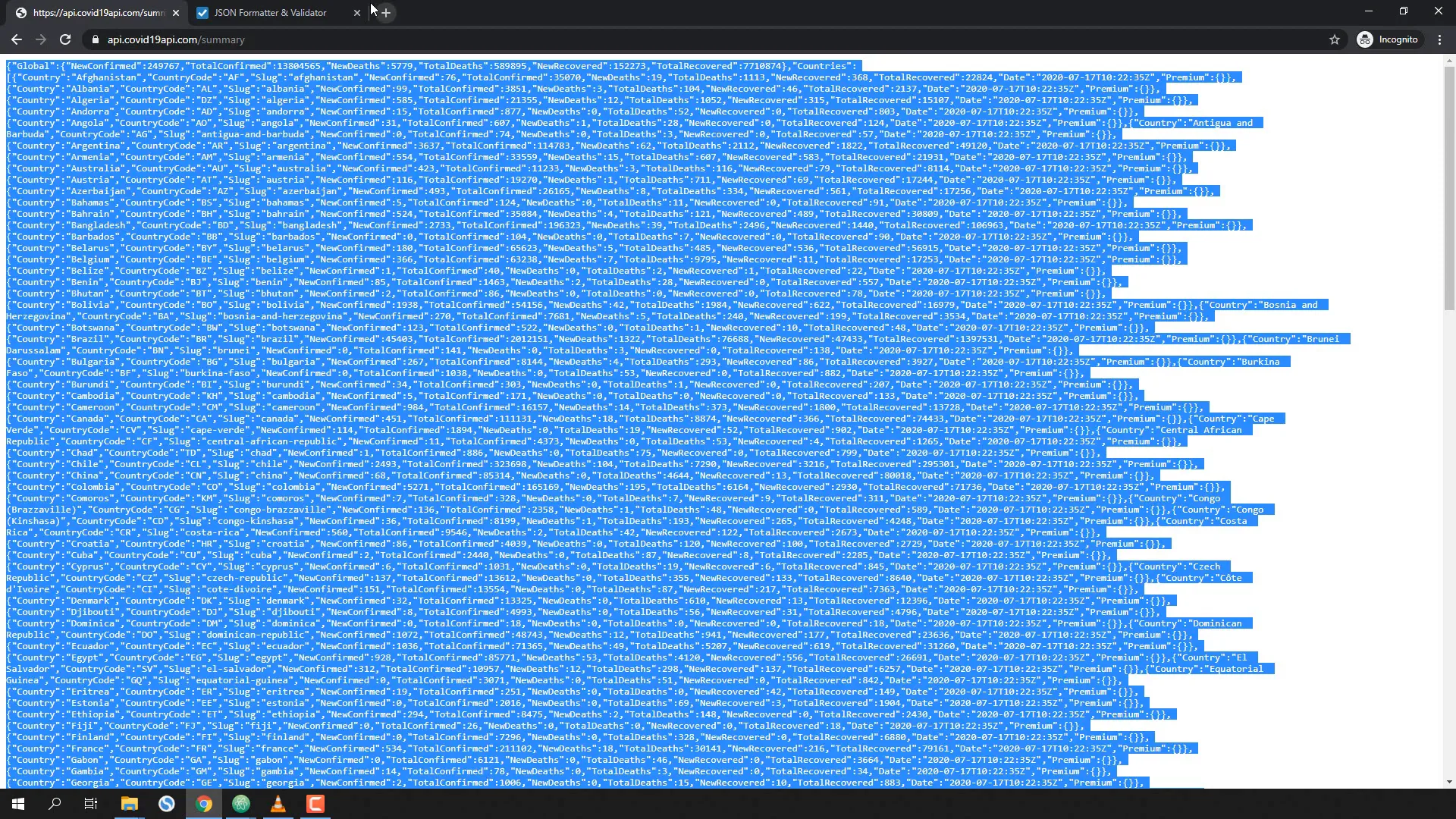
We will be using a COVID-19 API to fetch the necessary data. The output from the API is in JSON format, which we will parse in our application. The API URL is here.
Setting Up the Python Script
Start by creating a Python file named covid19_tutorial.py. We’ll need to import the requests and json libraries to handle our API calls.
Here’s how to set up the basic code to retrieve data:
- Import the necessary libraries: requests and json.
- Store the API URL in a variable called URL.
- Use the requests library to fetch the data.
- Parse the JSON response to a Python dictionary.
Retrieving COVID-19 Data
To access new confirmed cases for a specific country, you can create a variable called new_confirmed and set it to the corresponding data from the JSON response.
For example:
new_confirmed = data['Countries'][0]['NewConfirmed']This grabs the new confirmed cases for the first country in the list. To validate, check the API output in your browser.
Dynamic Country Search
Instead of hardcoding the index for the country, let’s create a function that dynamically retrieves the index based on user input. This function will take a country name as an argument and return the corresponding index.
Here’s how to do it:
def get_country_index(country):
for index, item in enumerate(data['Countries']):
if item['Country'] == country:
return indexTest this function with various country names to ensure it works correctly.
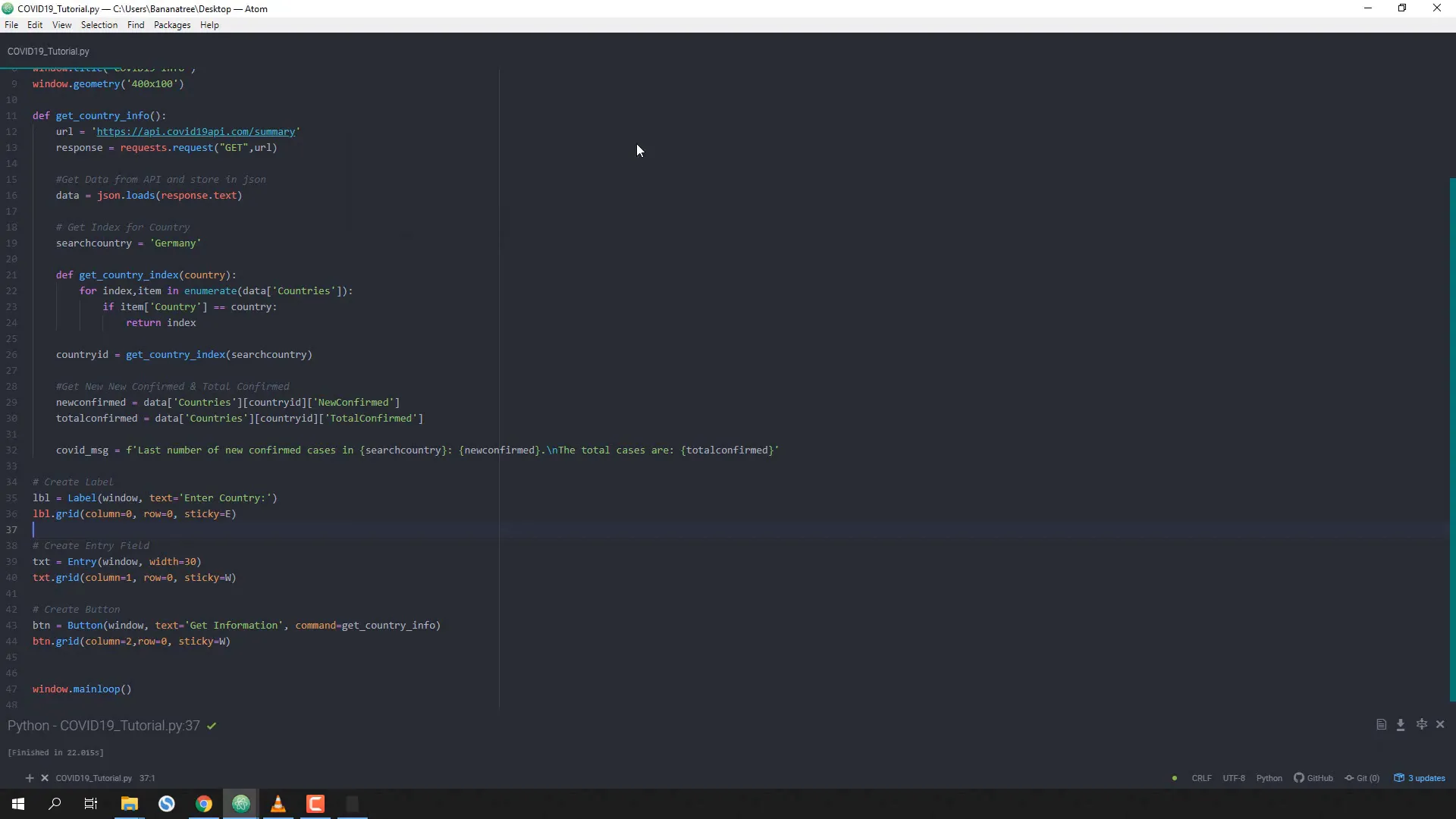
Building the GUI with Tkinter
Now, let’s create the GUI using Tkinter. First, initialize the main window:
Displaying the Output
To display the COVID-19 statistics in the GUI instead of the console, create another label for output:
output_text = StringVar()
output_label = Label(window, textvariable=output_text)
output_label.grid(column=0, columnspan=2, row=1, sticky=W)Finally, update the output text variable with the COVID-19 message:
output_text.set(covid_msg)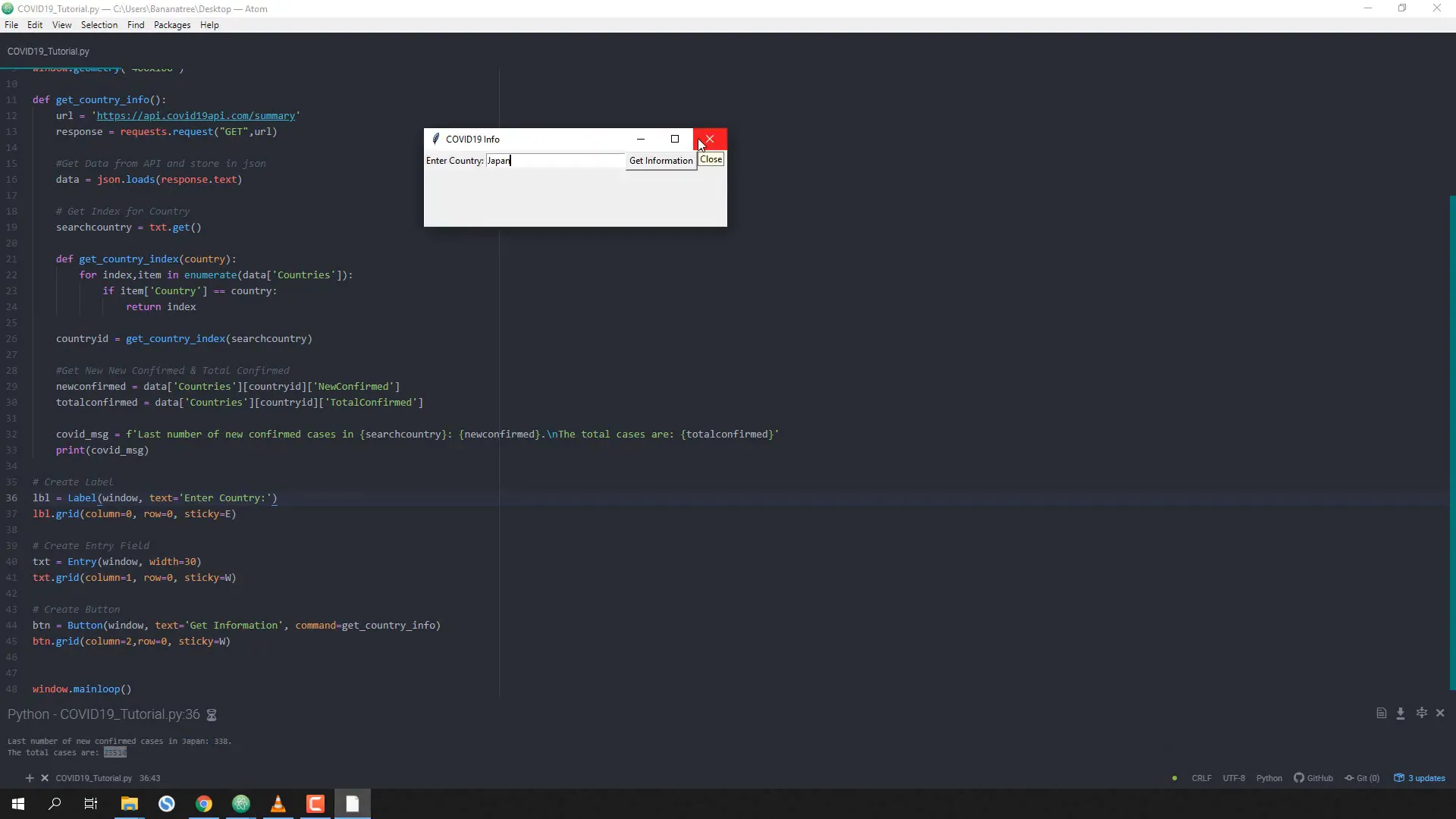
Final Touches
Once you have everything set up, run your script. You should now have a functional GUI that retrieves and displays COVID-19 statistics for any given country!
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I demonstrated how to create a simple GUI application using Python and Tkinter to fetch COVID-19 data from an API. This serves as a great starting point for beginners wanting to learn about API integration and GUI development.
Full Code
import requests
import json
from tkinter import *
window = Tk()
# Window Config
window.title('COVID19 Info')
window.geometry('400x100')
def get_country_info():
url = 'https://api.covid19api.com/summary'
response = requests.request("GET",url)
#Get Data from API and store in json
data = json.loads(response.text)
# Get Index for Country
searchcountry = txt.get()
def get_country_index(country):
for index,item in enumerate(data['Countries']):
if item['Country'] == country:
return index
countryid = get_country_index(searchcountry)
#Get New New Confirmed & Total Confirmed
newconfirmed = data['Countries'][countryid]['NewConfirmed']
totalconfirmed = data['Countries'][countryid]['TotalConfirmed']
covid_msg = f'Last number of new confirmed cases in {searchcountry}: {newconfirmed}.\nThe total cases are: {totalconfirmed}'
# Return covid msg to gui
output_text.set(covid_msg)
# Create Label
lbl = Label(window, text='Enter Country:')
lbl.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=E)
# Create Entry Field
txt = Entry(window, width=30)
txt.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky=W)
# Create Button
btn = Button(window, text='Get Information', command=get_country_info)
btn.grid(column=2,row=0, sticky=W)
# Display Output
output_text = StringVar()
lbl_output = Label(window, textvariable=output_text)
lbl_output.grid(column=0,columnspan=2, row=1, sticky=W)
window.mainloop()


