Export a Pandas Dataframe to Excel with Document Properties
Introduction
In this post, I will walk you through the process of exporting a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file while also setting various document properties. This technique is useful for adding additional metadata to your Excel workbooks, such as the name of the Python file or Jupyter Notebook used to generate the spreadsheet.
Before diving into the coding part, ensure you have the necessary dependencies installed. To set Excel document properties, I will use the XlsxWriter package. You can easily install it via pip.
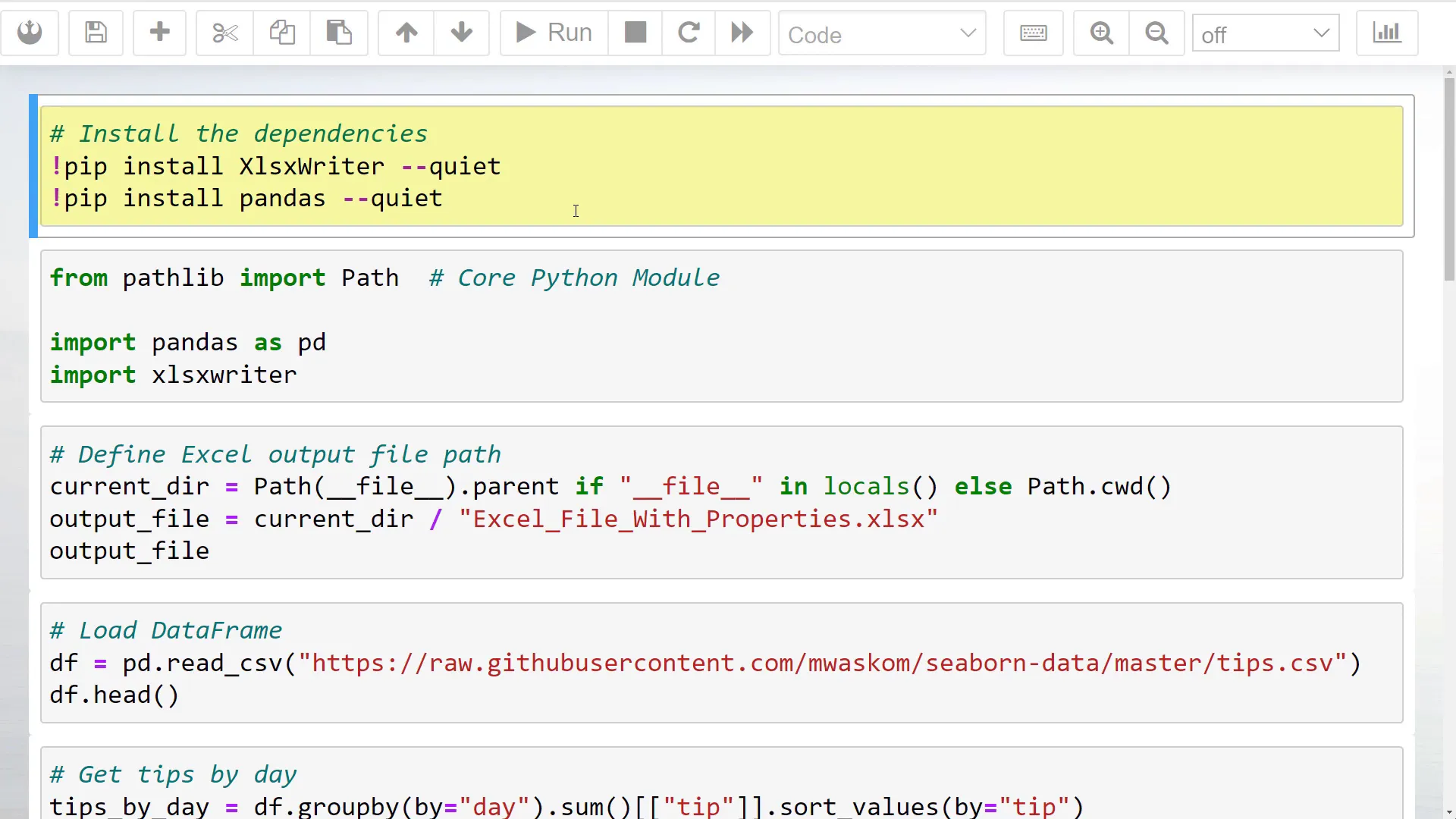
Once installed, I will import both xlsxwriter and pandas as pd. Additionally, I will import Path from pathlib to handle file paths.
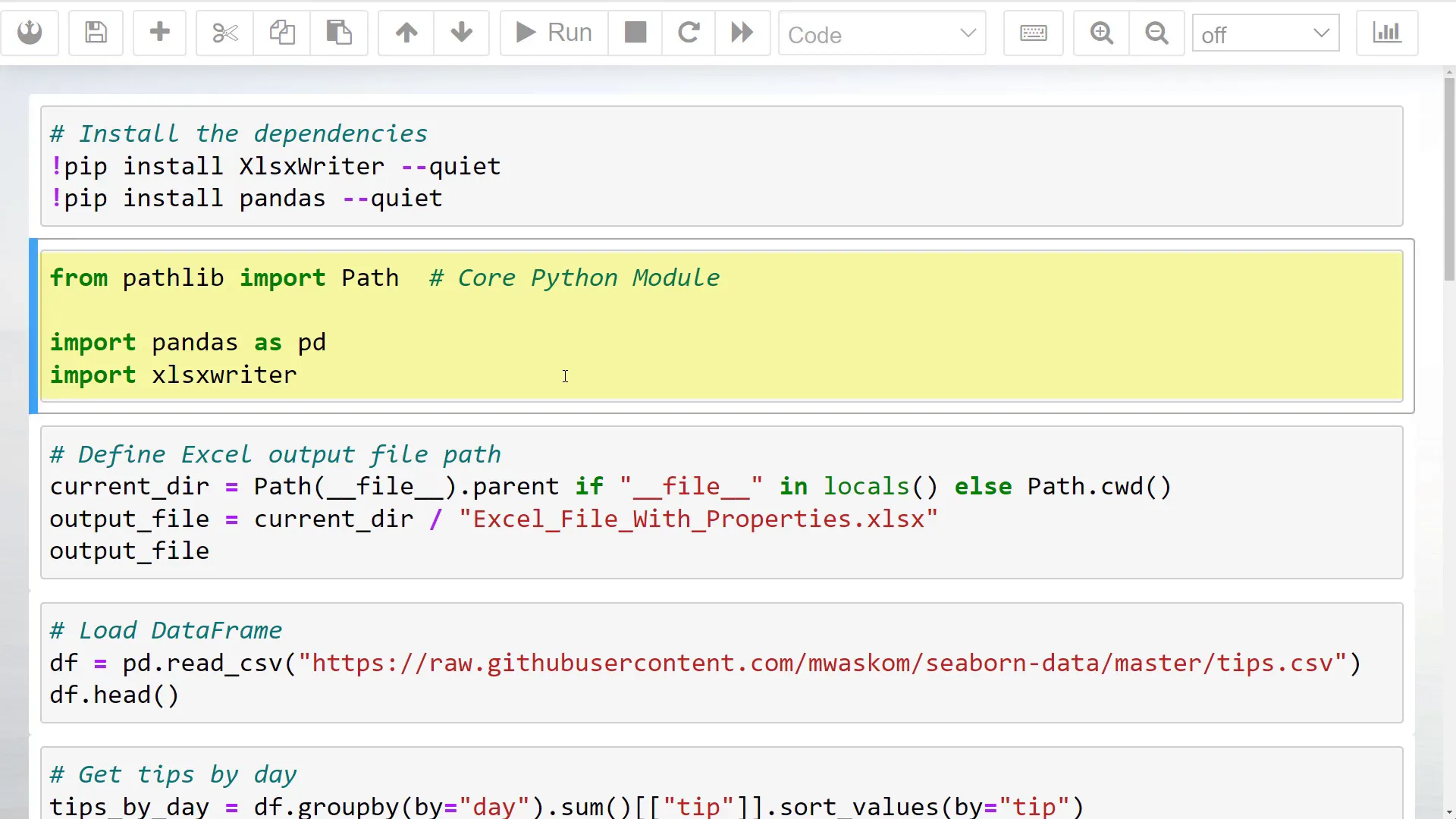
Pathlib is a core Python module, so you do not need to install it separately. Now, let’s define the current working directory, which is where our Jupyter Notebook is located. I’ve included an if-statement to ensure it works in both Jupyter Notebooks and standard Python files.
Coding out the solution
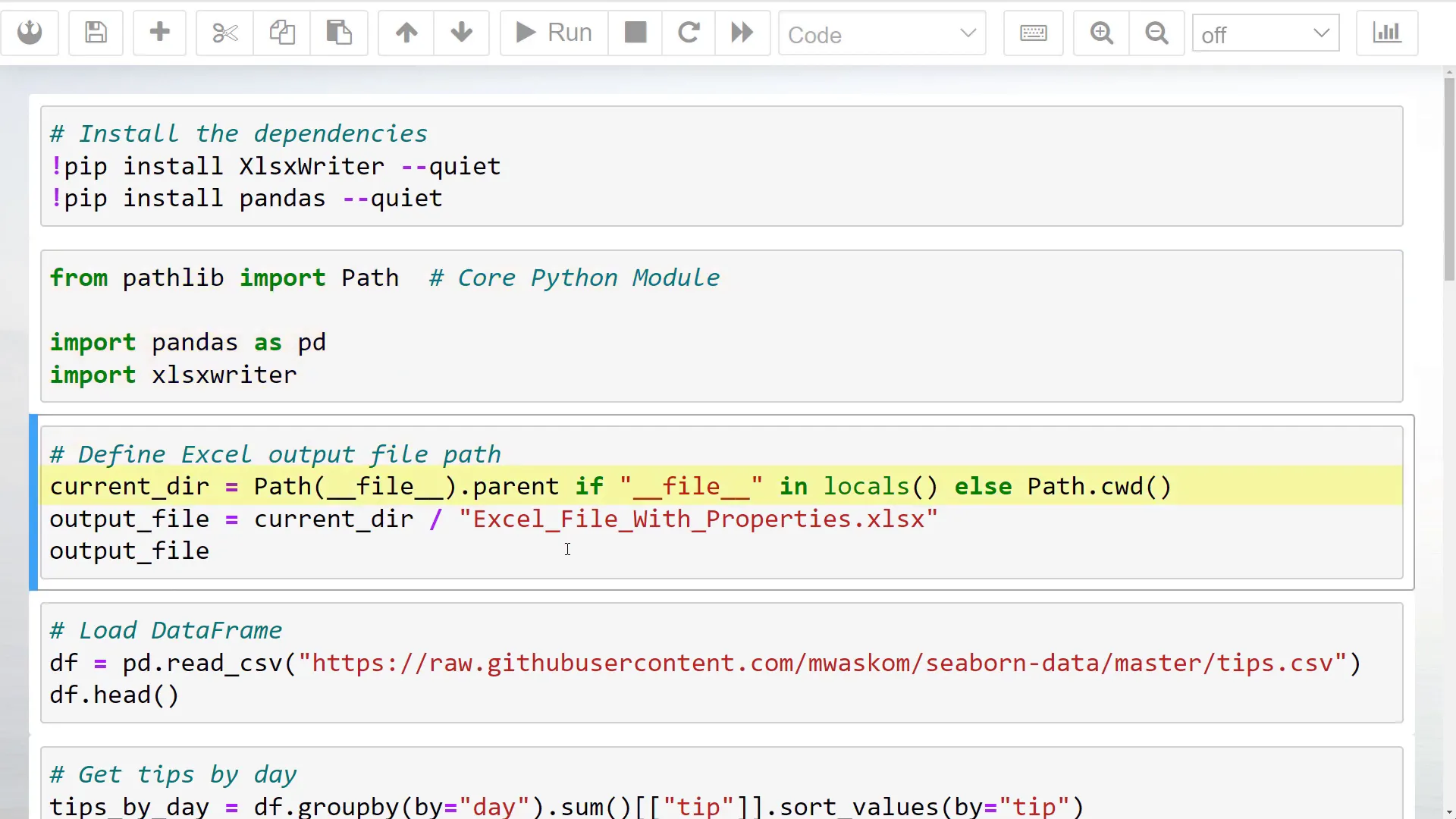
Next, I will specify the output file path where the generated Excel file will be saved. For this example, I will create a sample Pandas DataFrame using the tips dataset from the Seaborn library, which is available on GitHub.
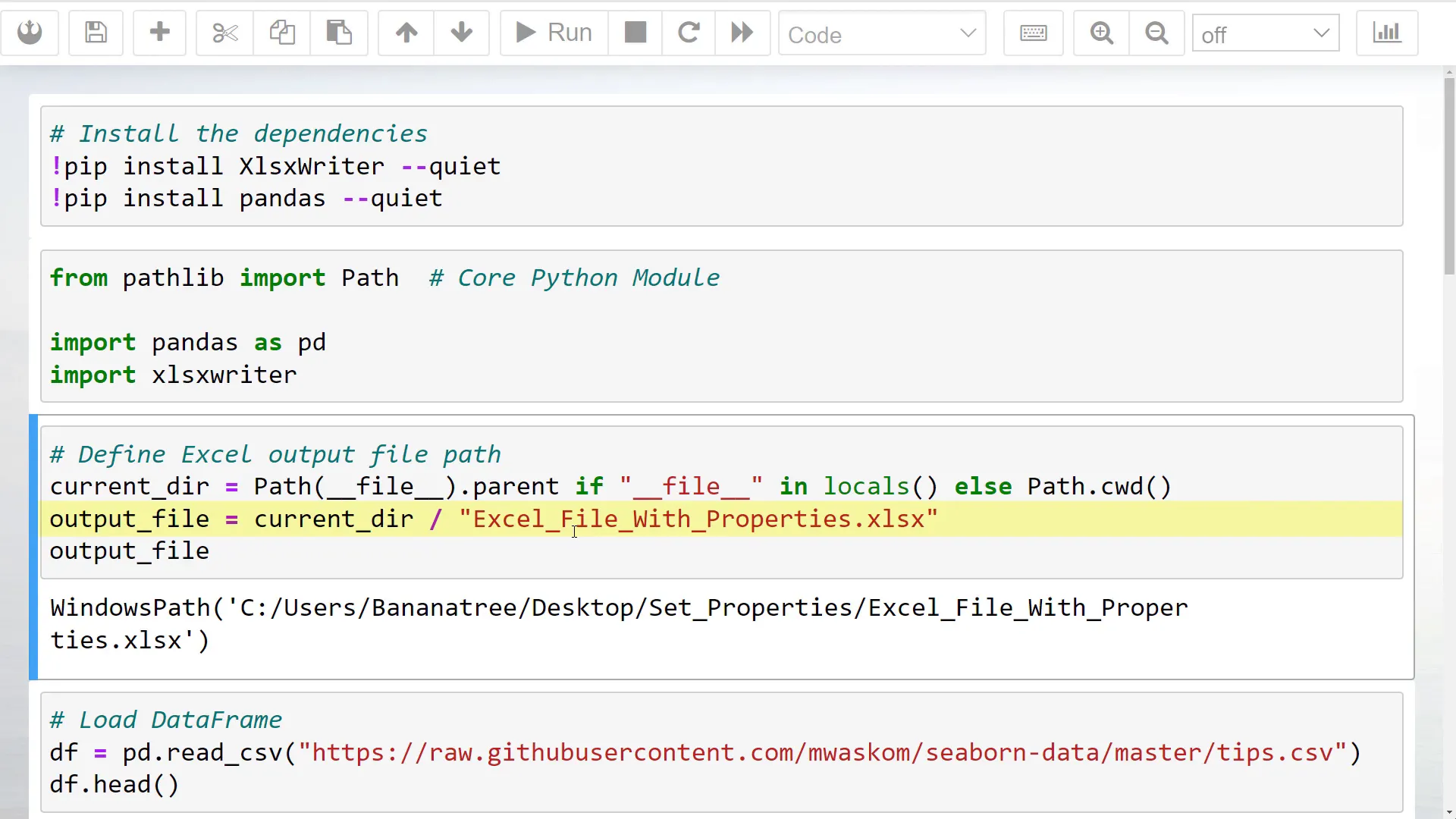
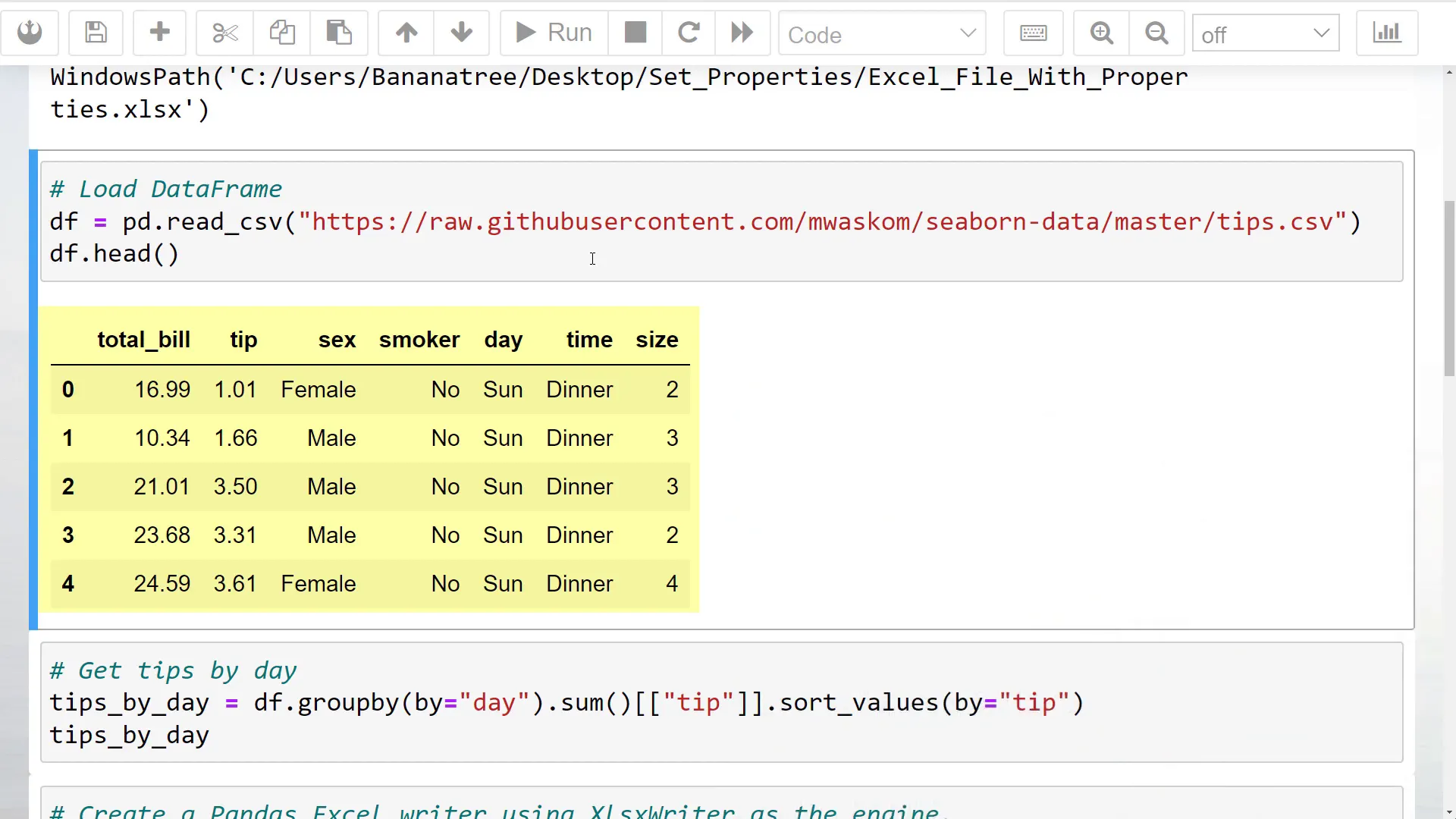
The dataset contains information like total bill and tip amount, along with customer details such as gender and group size. I will sum up the tips by day and sort the values by tip size to create our DataFrame.
Now, let’s export this DataFrame to Excel. Typically, you would use df.to_excel followed by the output file path. However, to set the document properties, we will utilize the XlsxWriter package.
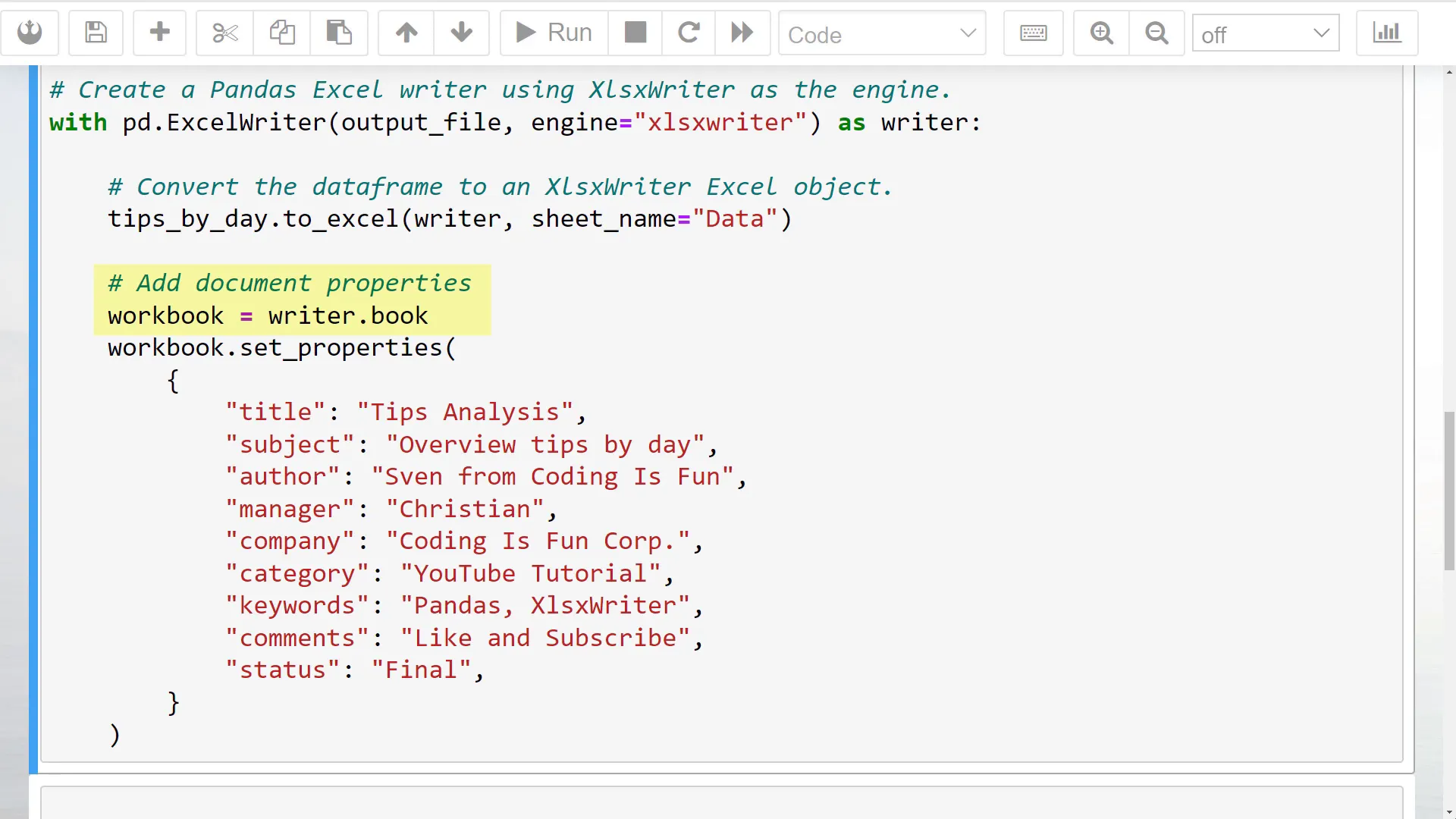
First, I will open the Pandas Excel writer object in a context manager, specifying the output file path and the engine.
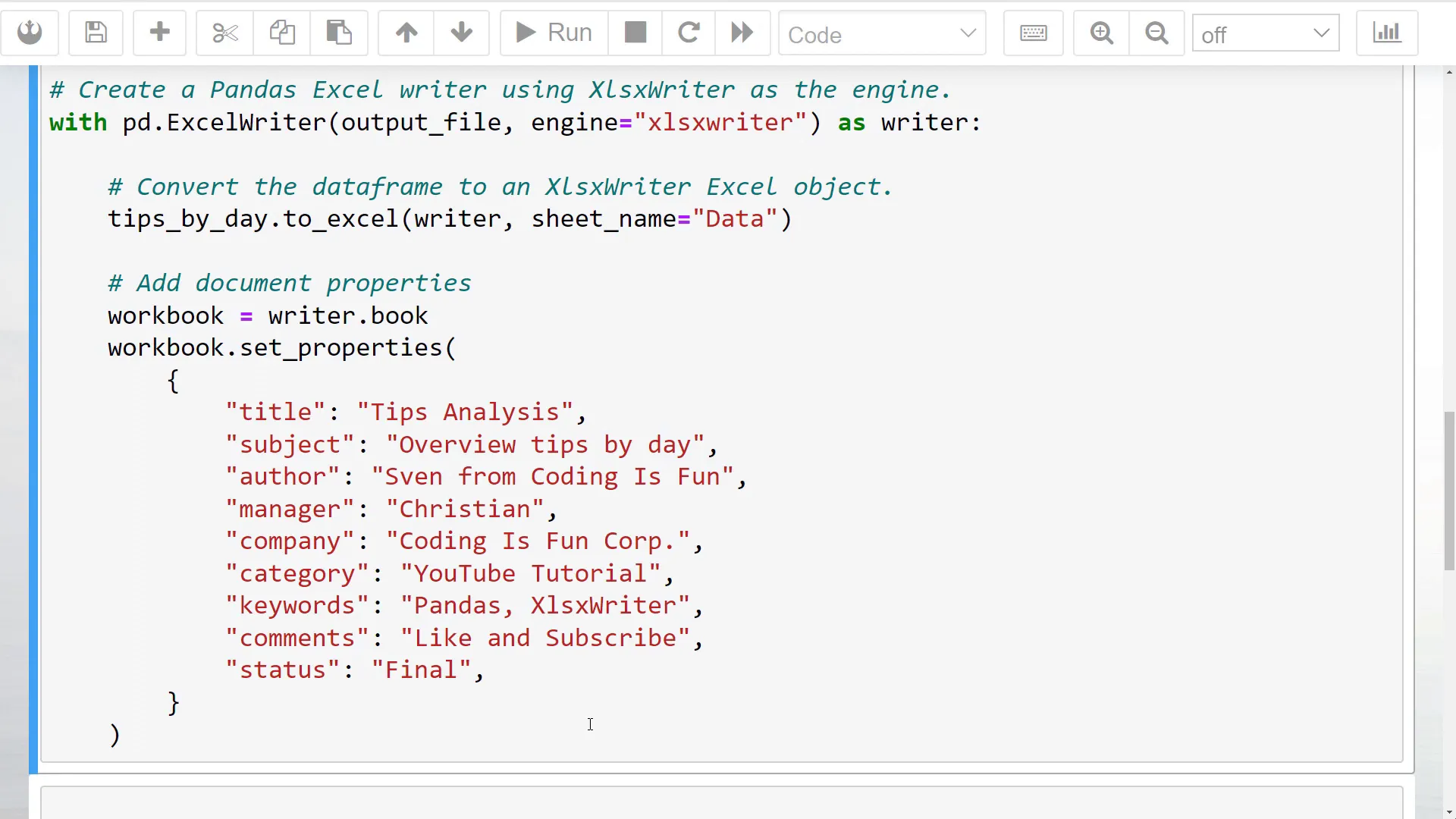
Next, I will use the to_excel method, passing in the writer object instead of the filename. Additionally, I will provide a sheet name.
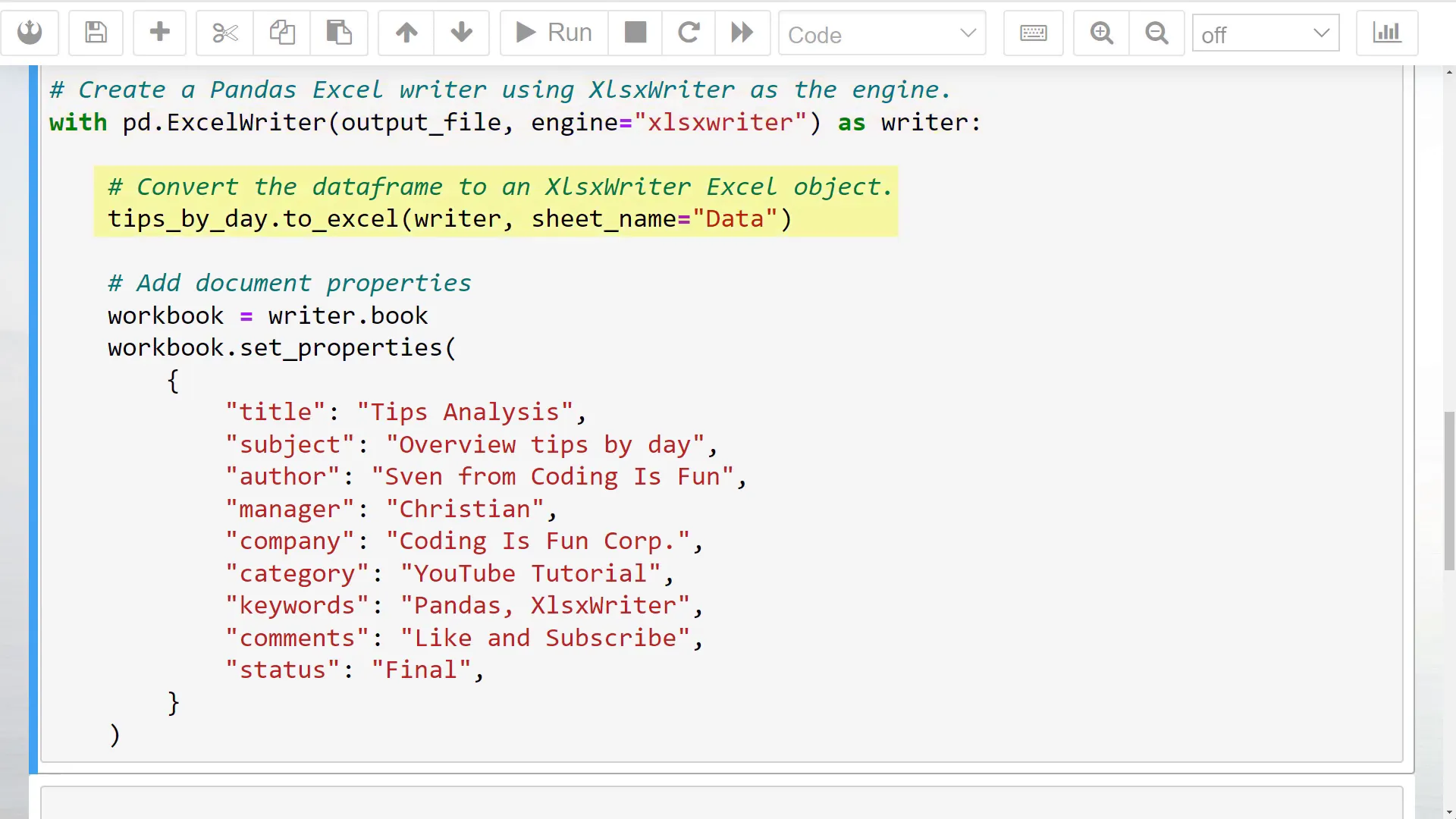
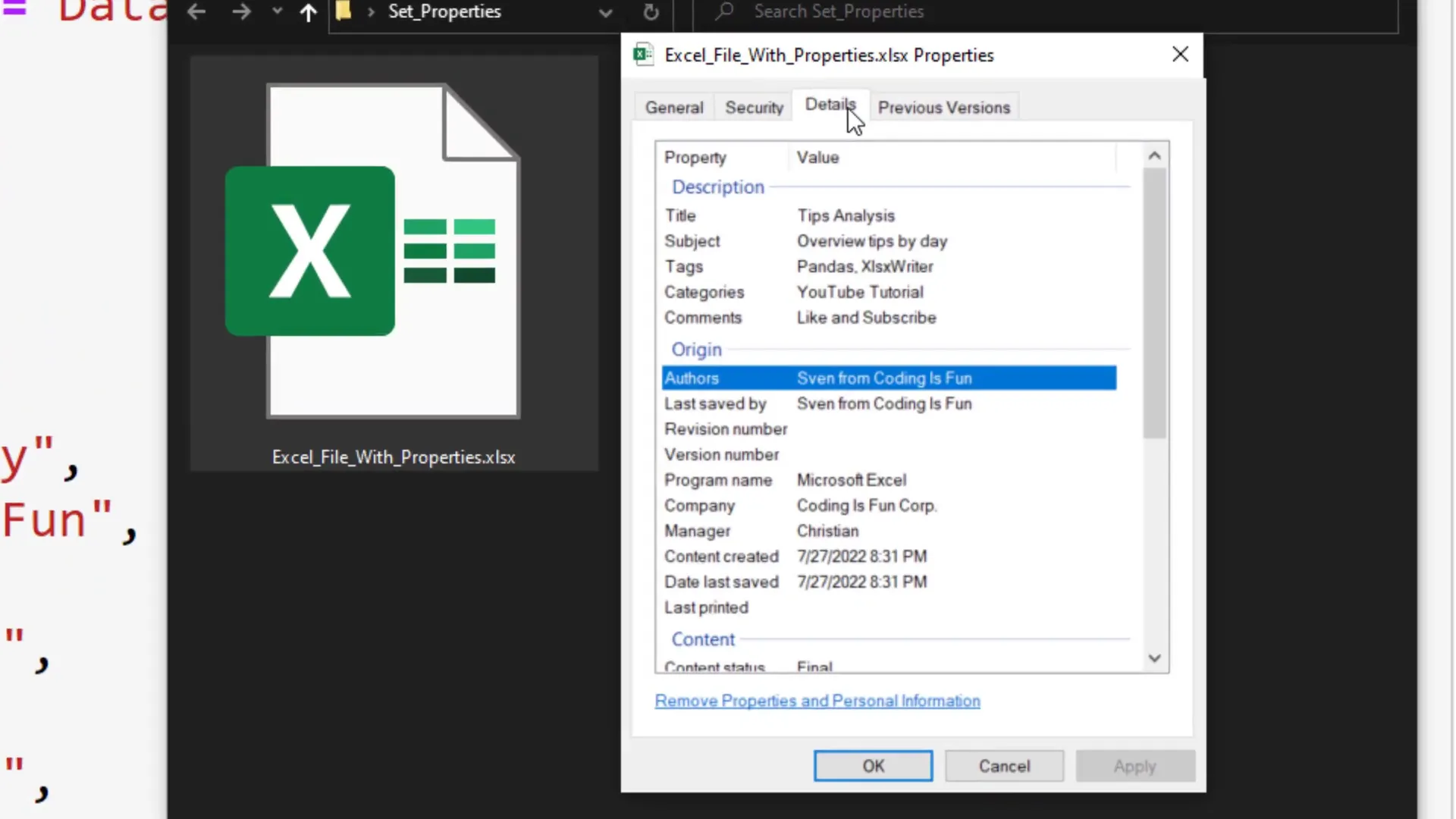
To add the document properties, we need to access the workbook by typing writers.book. I have listed several properties you can set, including title, subject, author, manager, company, category, keywords, comments, and status. Feel free to include only the fields you need.
After running this cell, you should find a new workbook in your current working directory. If you open this file, you will see the DataFrame we generated earlier.
To check the document properties, right-click on the file and select properties. You can view the details under the ‘details’ tab.
Outro
And that’s it for this tutorial! This is just one example of how to use the XlsxWriter package in combination with Pandas to enhance your Excel files. Thank you for reading!