How to Automate Excel with Python (Crash Course)
Introduction
Automating tasks in Excel can save a lot of time and effort. With Python and xlwings, I can easily connect to Excel, read and write data, and even create reports. This blog will guide you through the steps to automate Excel with Python, from installation to practical examples.
Installing Dependencies
Before I can start automating Excel, I need to install the necessary packages. The primary package I need is xlwings. I can install it using pip:
pip install xlwings
Connecting to an Excel Workbook
Once I have xlwings installed, connecting to an Excel workbook is straightforward. There are three different scenarios. Connecting to a new, unsaved or saved workbook. 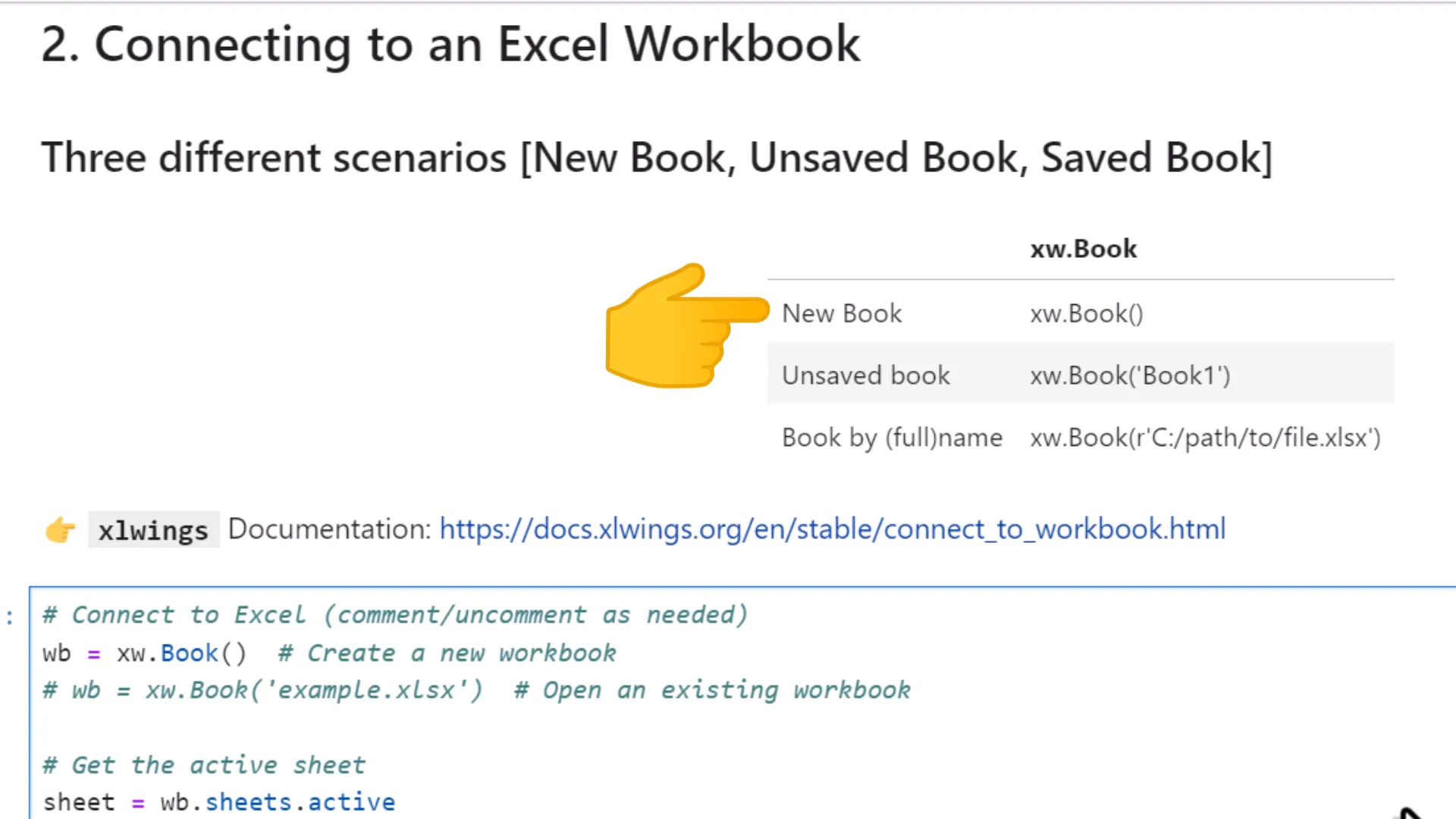
Writing and Reading Data in Excel
With the connection established, I can start writing data to cells. For example, I can input values into specific cells in the workbook. I can also read the values back to confirm they were saved correctly.
Using Ranges and Formulas
Using ranges makes it easy to manipulate data. I can select multiple cells and apply formulas to them. This is useful for calculations, like summing or averaging data points directly in the spreadsheet.
Integrating Pandas for Data Analysis
For more complex data analysis, I can integrate the Pandas library. This allows me to load data into a DataFrame, perform analysis, and then write results back to Excel. Pandas makes data manipulation much easier.
Saving and Closing Workbooks
After I’ve made changes, I need to save my work. I can do this easily with xlwings. Closing the workbook properly ensures that all my changes are saved without any issues.
Using the Context Manager
To manage resources better, I can use a context manager with xlwings. This approach automatically handles opening and closing the workbook, which adds a layer of safety to my automation tasks. 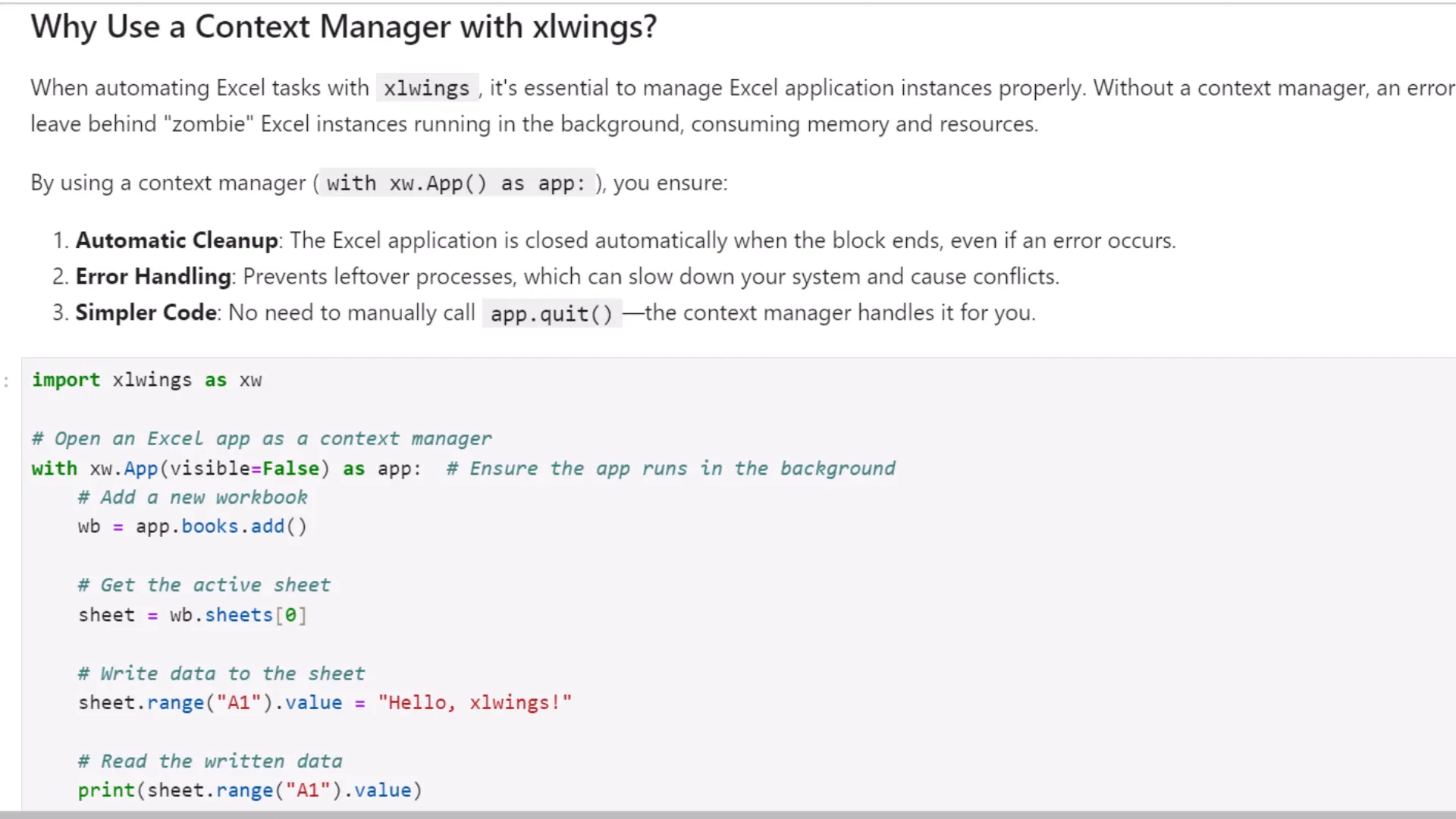
Practical Example: Creating a Stock Report
One practical use of this automation is creating a stock report. I can pull data from various sources, process it, and then generate a report in Excel. This example shows how effective automation can be for business tasks. 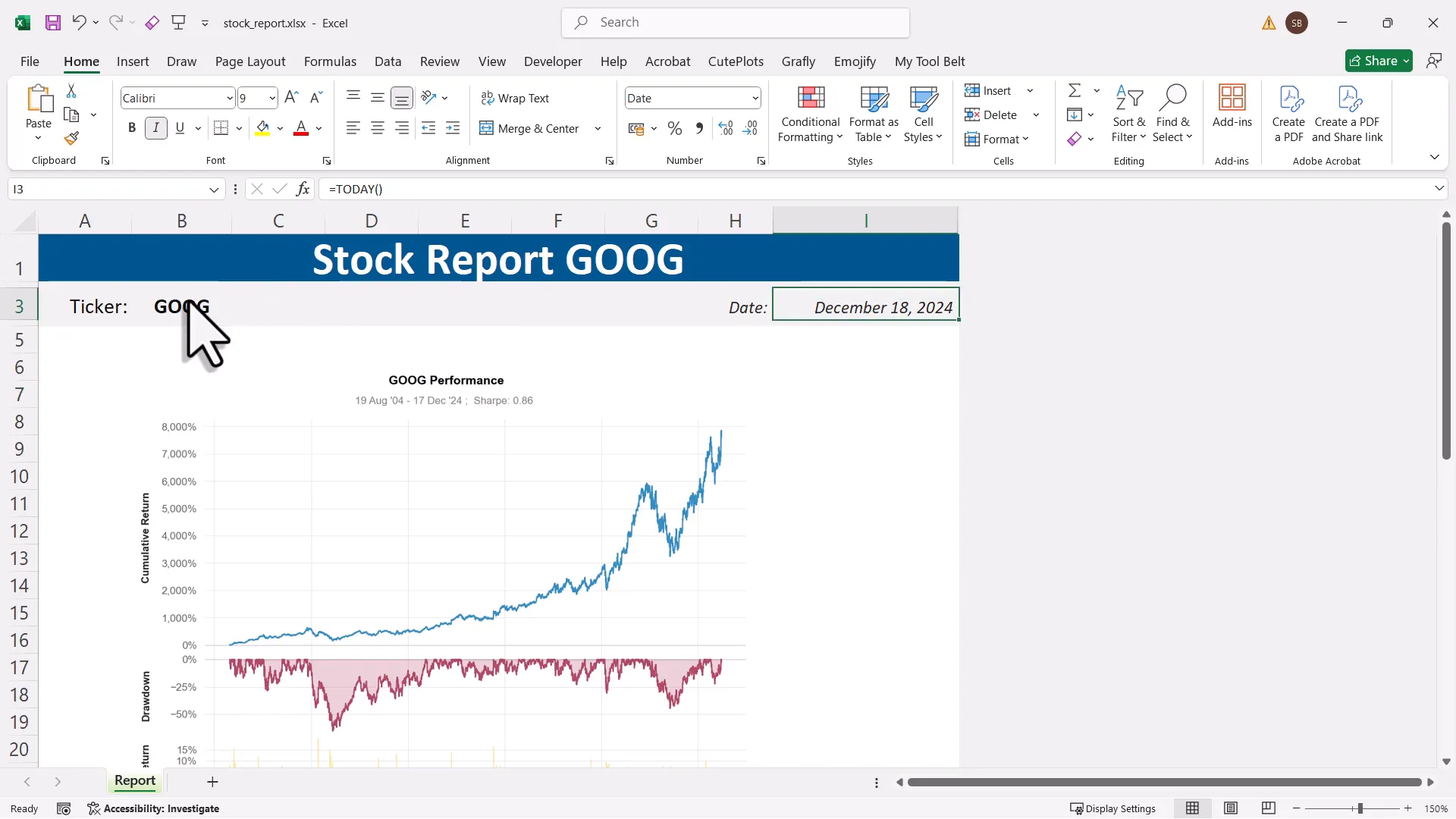
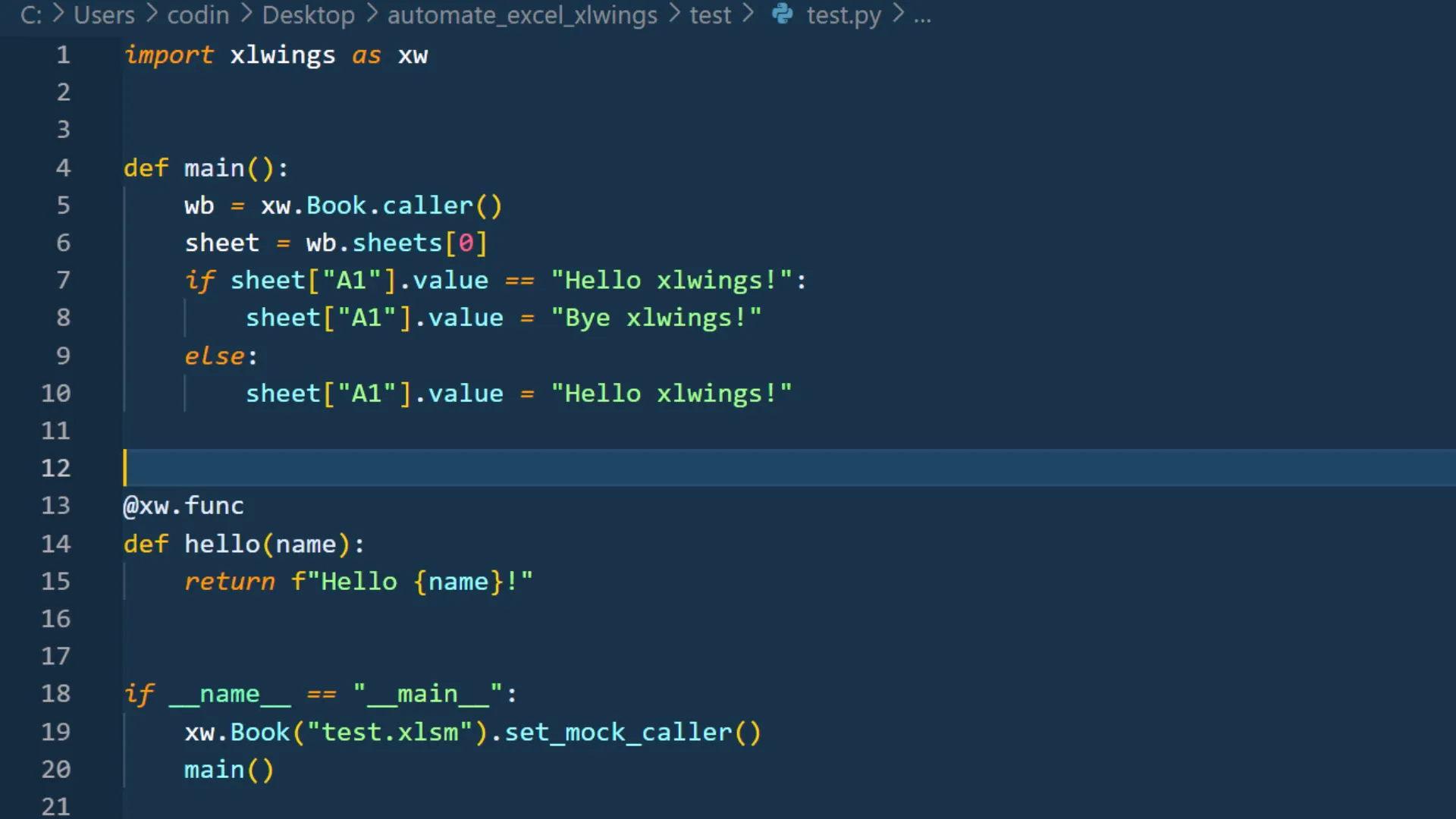
Triggering Python Scripts Directly from Excel
I can also trigger my Python scripts directly from Excel. This means my coworkers can run the automation tasks without needing to know Python, making it user-friendly and efficient. For that, you can create a quickstart project as shown below: Then in the quickstart project, you can add the “Sample Call” macro to a button to execute the Python file in the same directory:
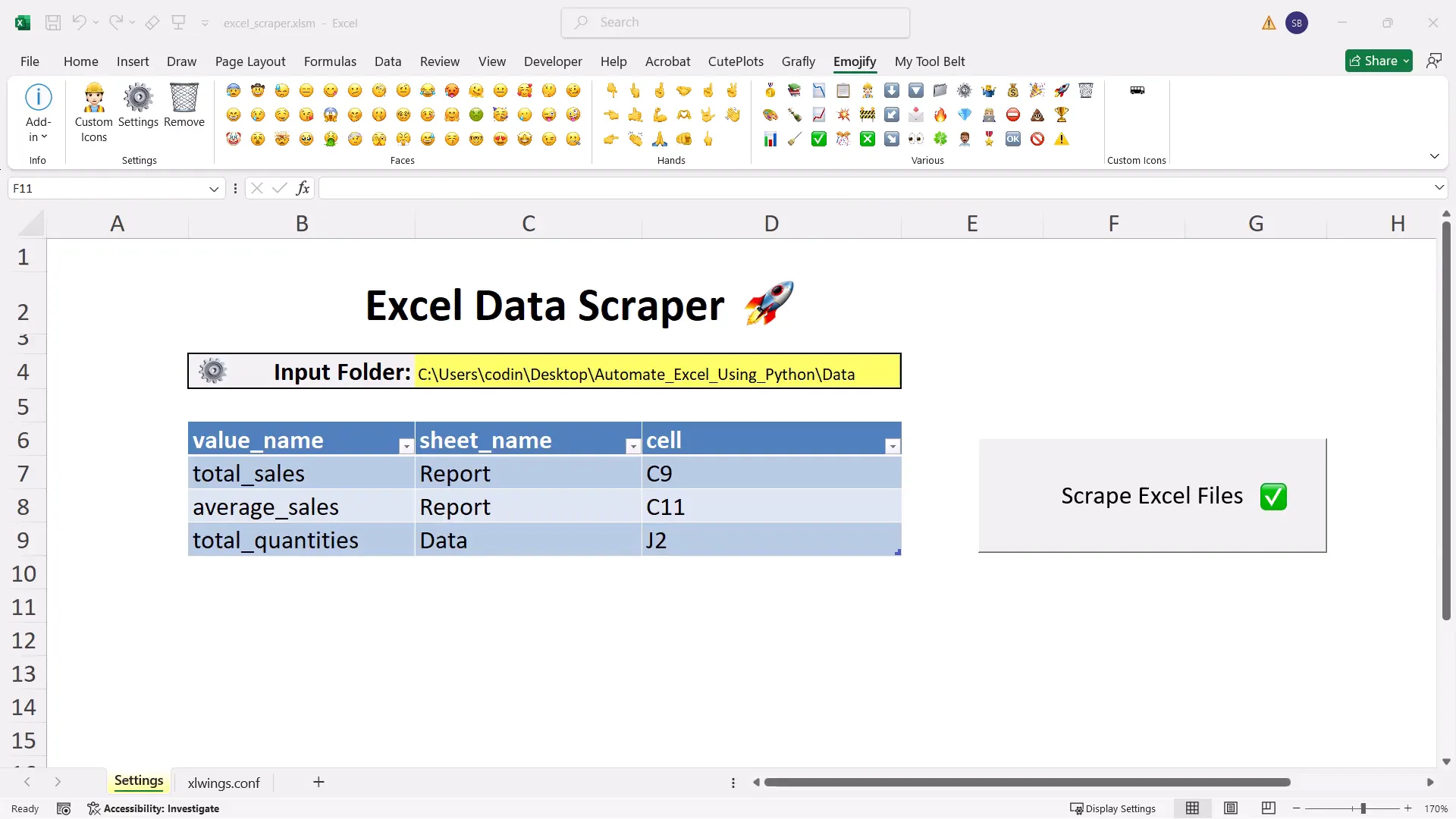
Practical Example: Automating Excel Data Scraping
Another useful example is automating data scraping from Excel. I can set up scripts that pull data from various online sources and populate my Excel sheets automatically. This saves a lot of manual effort.
Upcoming Excel Automation Course
I’m excited to announce that I have an upcoming course focused on Excel automation. This course will cover everything from the basics to advanced techniques, helping you become proficient in automating your tasks.
Conclusion
Automating Excel with Python is a powerful way to improve efficiency and accuracy in handling data. By following these steps, I can easily connect to Excel, manipulate data, and create useful reports. This approach not only saves time but also enhances productivity.