Weighted Average Calculation in Pandas
Introduction
In this tutorial, I will walk you through the process of calculating a weighted average using the Pandas library in Python. This method is particularly useful for educators or anyone needing to evaluate scores that have different levels of importance.
Understanding Weighted Averages
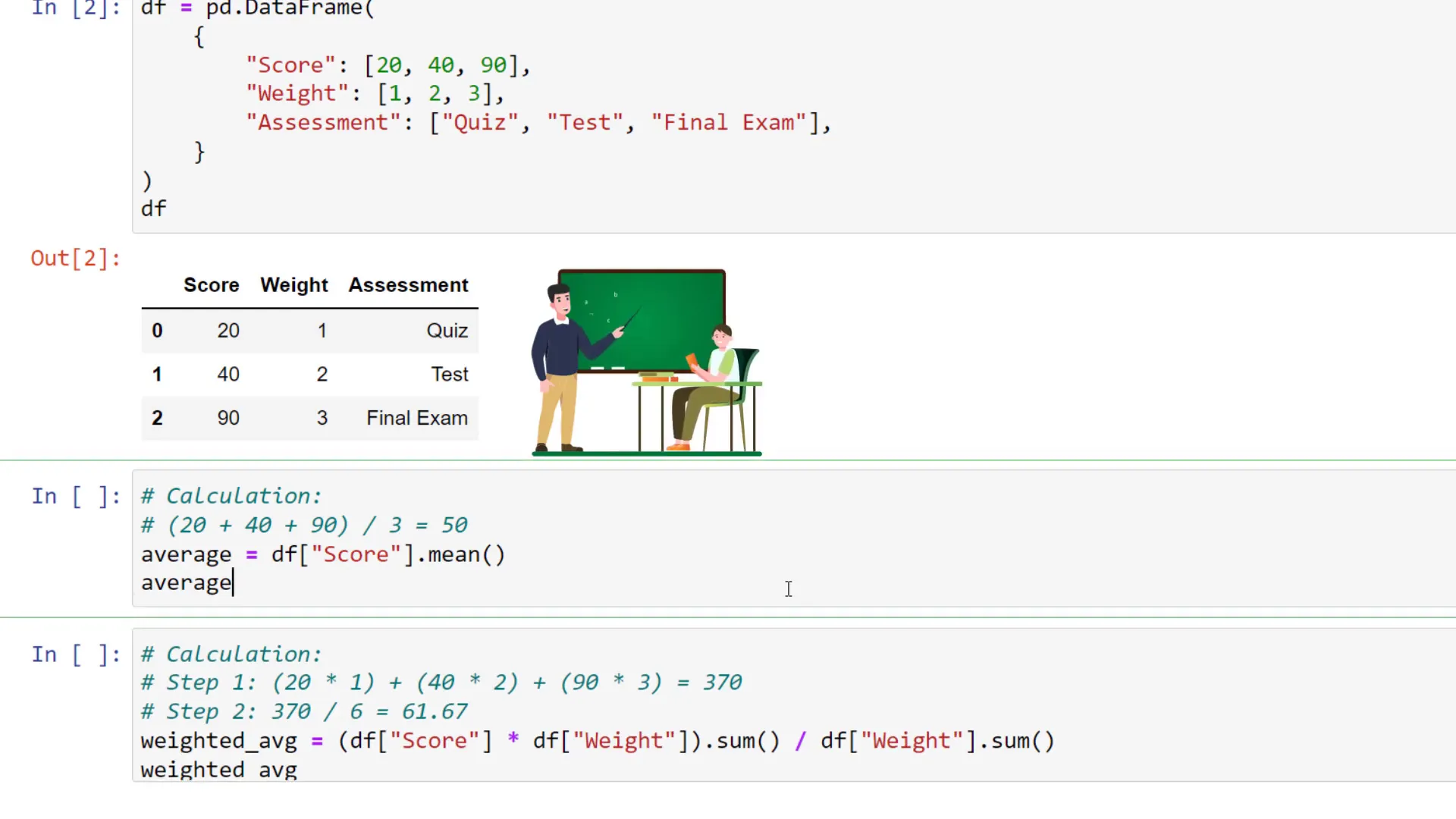
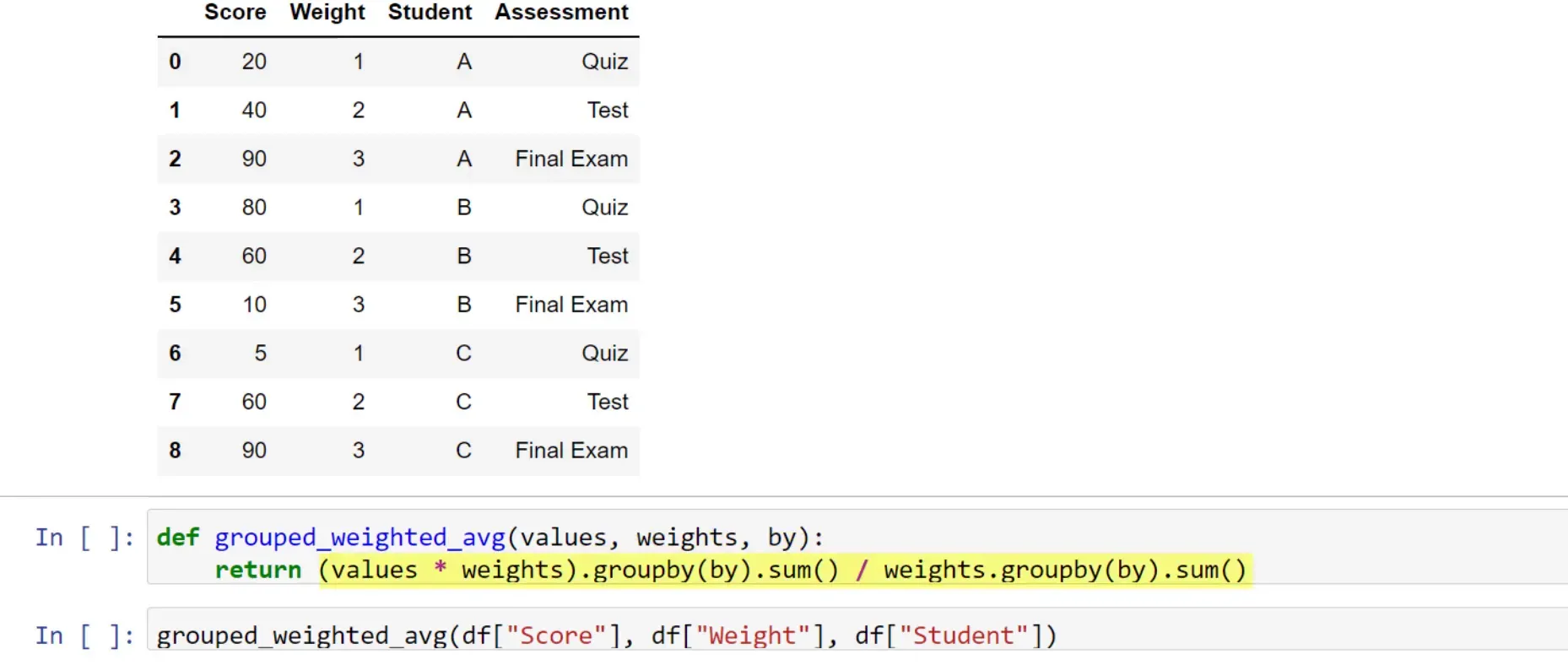
Imagine you are a teacher evaluating your students’ scores based on three different assessments: a quiz, a test, and a final exam. Each assessment has a different weight, influencing the overall score differently. Instead of calculating a simple mean, we want to compute the weighted average.
Calculation Logic
The calculation logic is straightforward:
- First, multiply each score by its respective weight. For example:
- Quiz: 20 * 1
- Test: 40 * 2
- Final Exam: 90 * 3
- Then, divide the total of these products by the sum of the weights.
Implementing in Pandas
To implement this in Pandas, you can easily perform vectorized calculations. Start by multiplying the scores by the weights and then calculating the sum. Finally, divide this result by the sum of the weights.
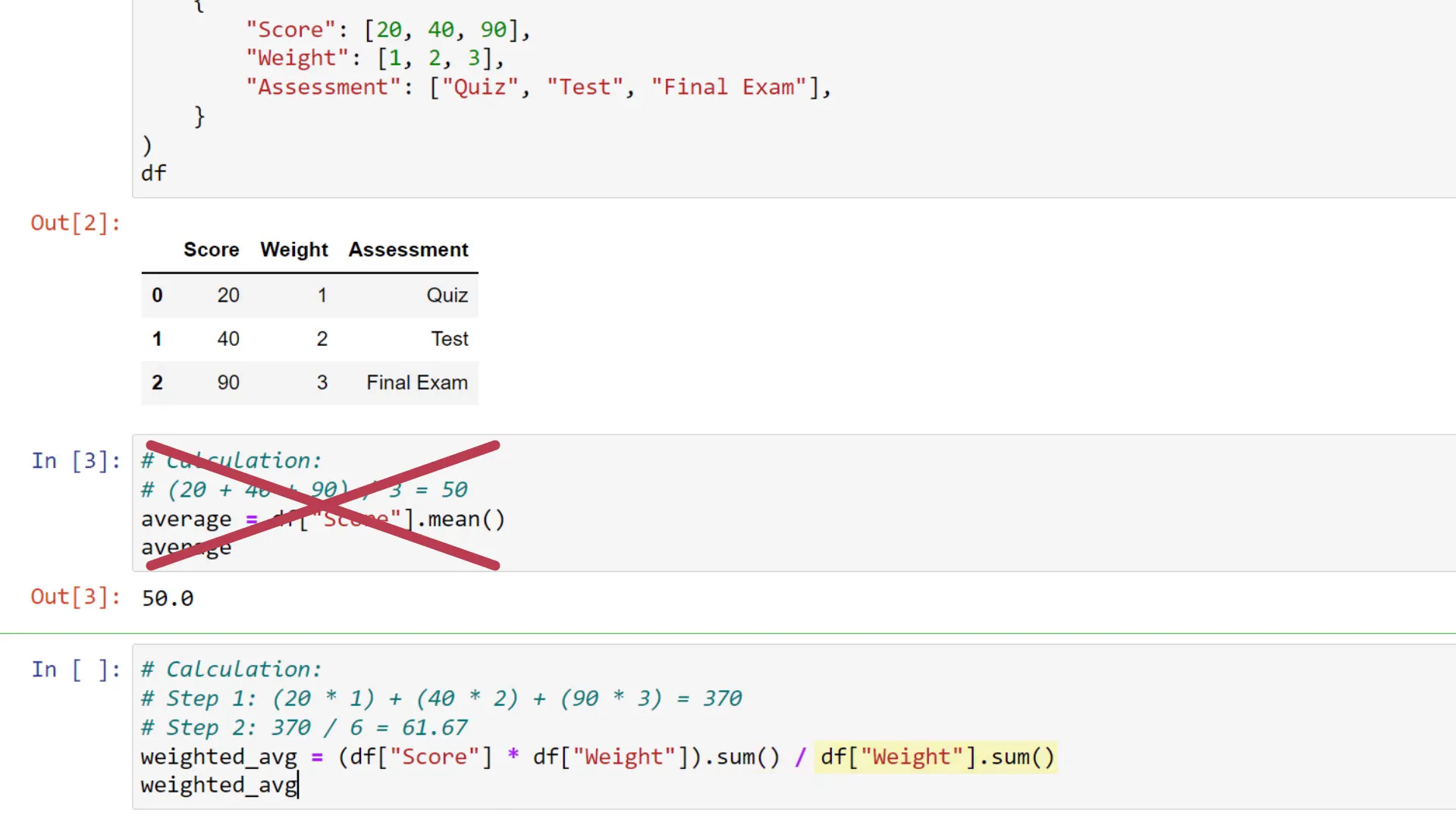
For the given DataFrame, the weighted average would be calculated as follows:
Weighted Average = (20*1 + 40*2 + 90*3) / (1 + 2 + 3) = 61.67
Calculating Weighted Averages for Specific Students
For the next example, I added a column for different students. Let’s say you want to calculate the weighted average only for Student B. You can filter your data using the query method.
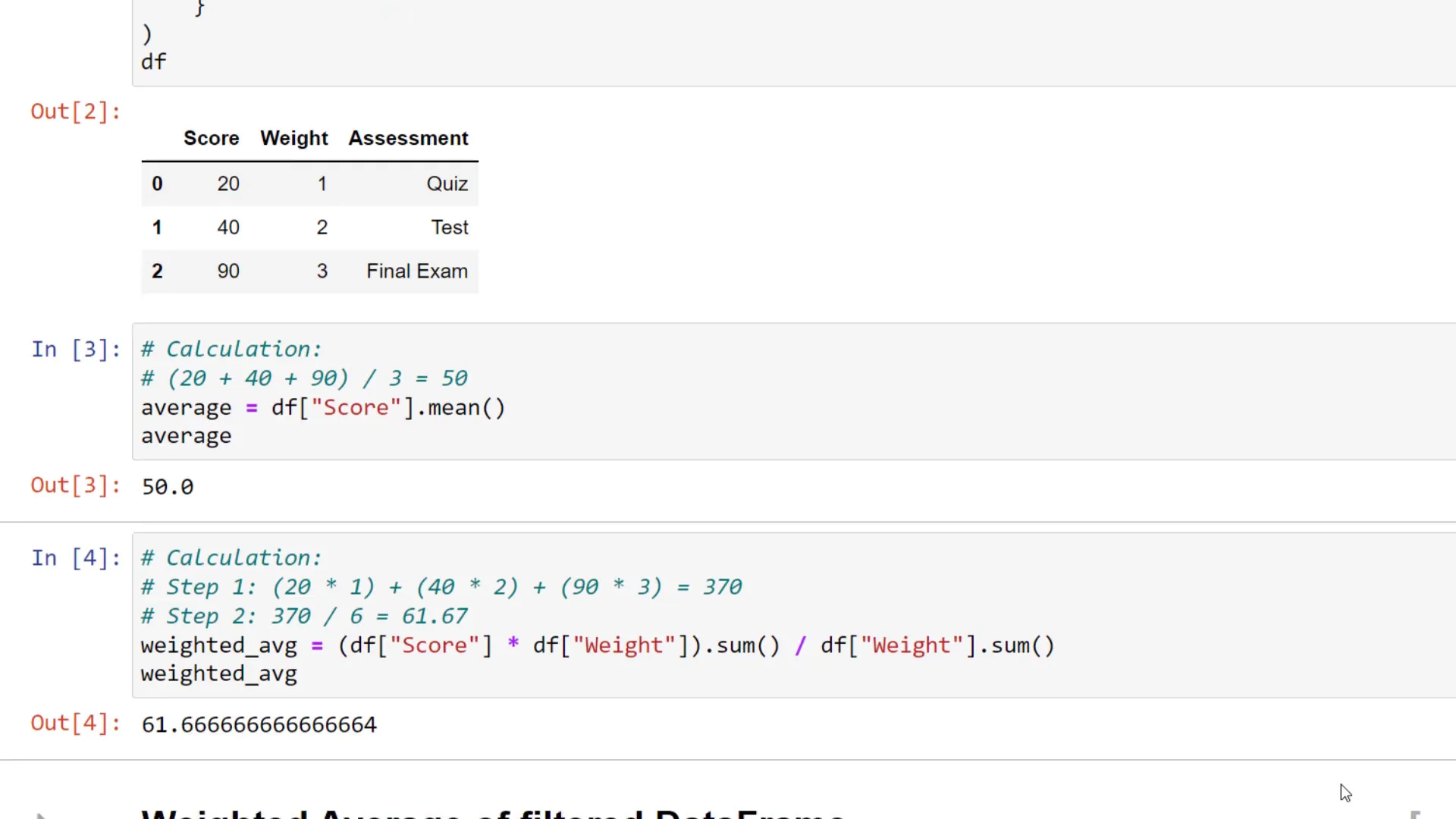
The filtered DataFrame will look like this:
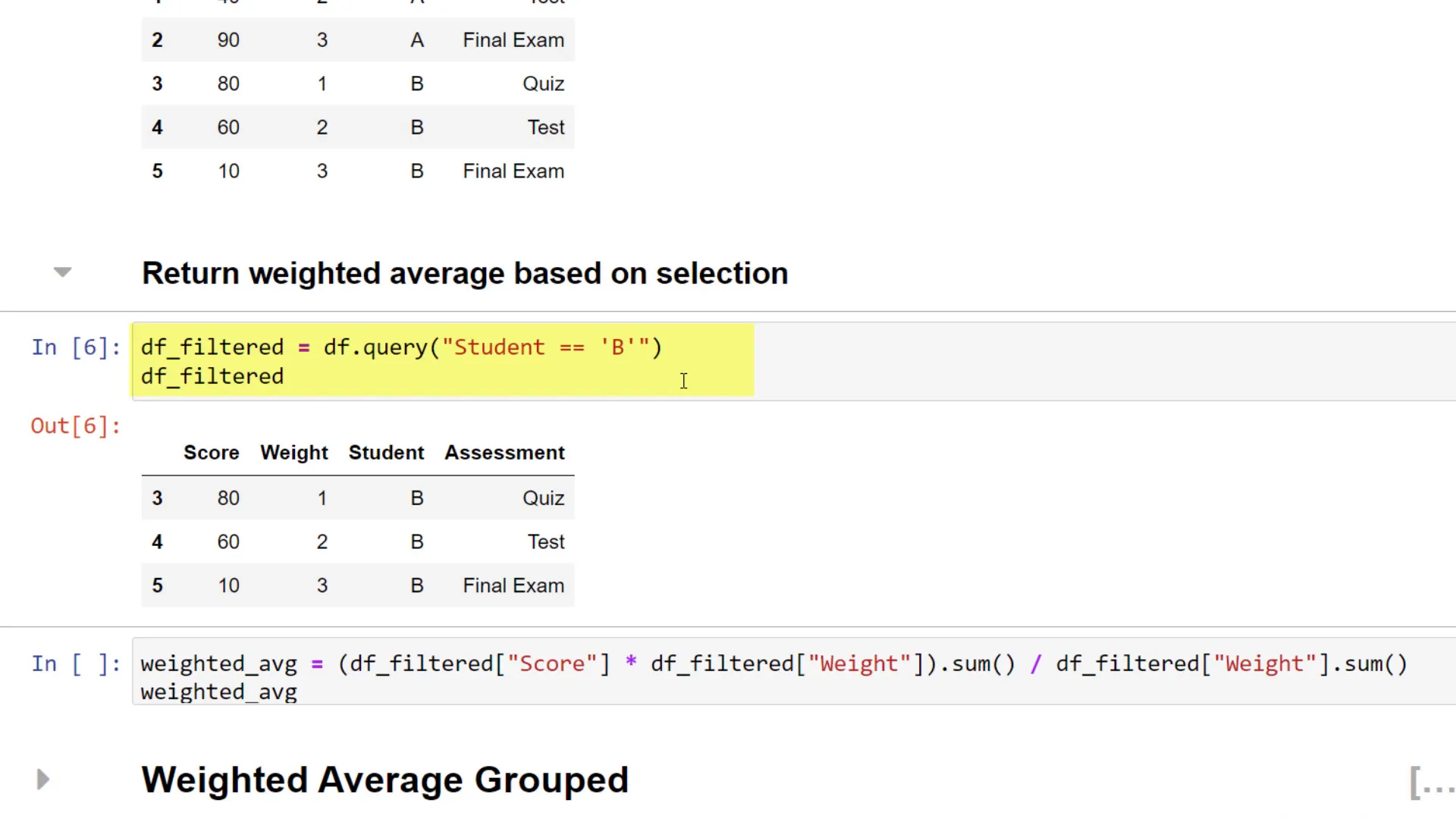
With the filtered data in place, you can apply the same calculation. However, this method can become tedious with larger datasets, especially if you have many students.
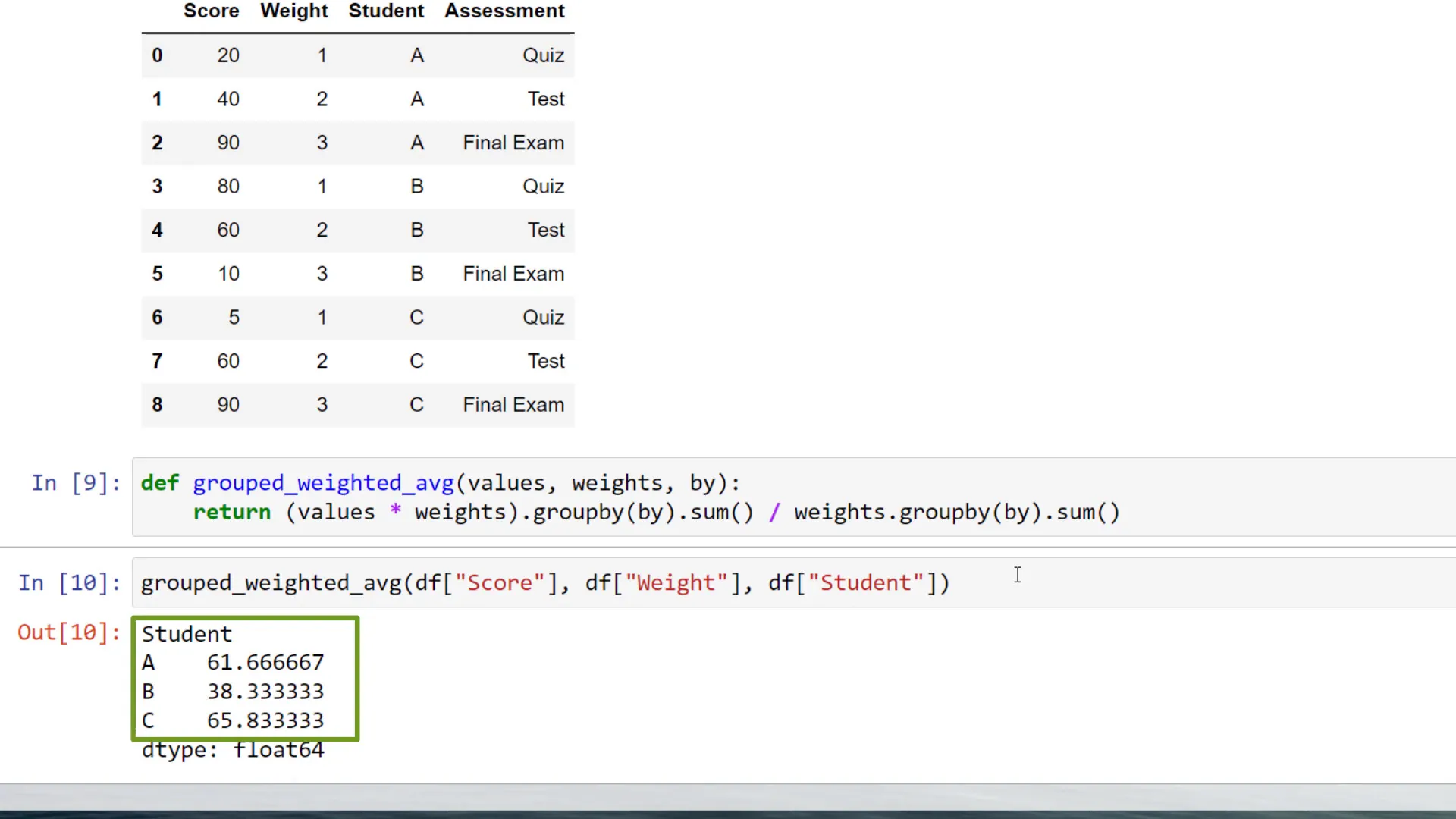
Using a Helper Function
Instead, I recommend creating a small helper function. This function will take three parameters: the values (scores), the weights, and the column name by which you want to group the weighted average.
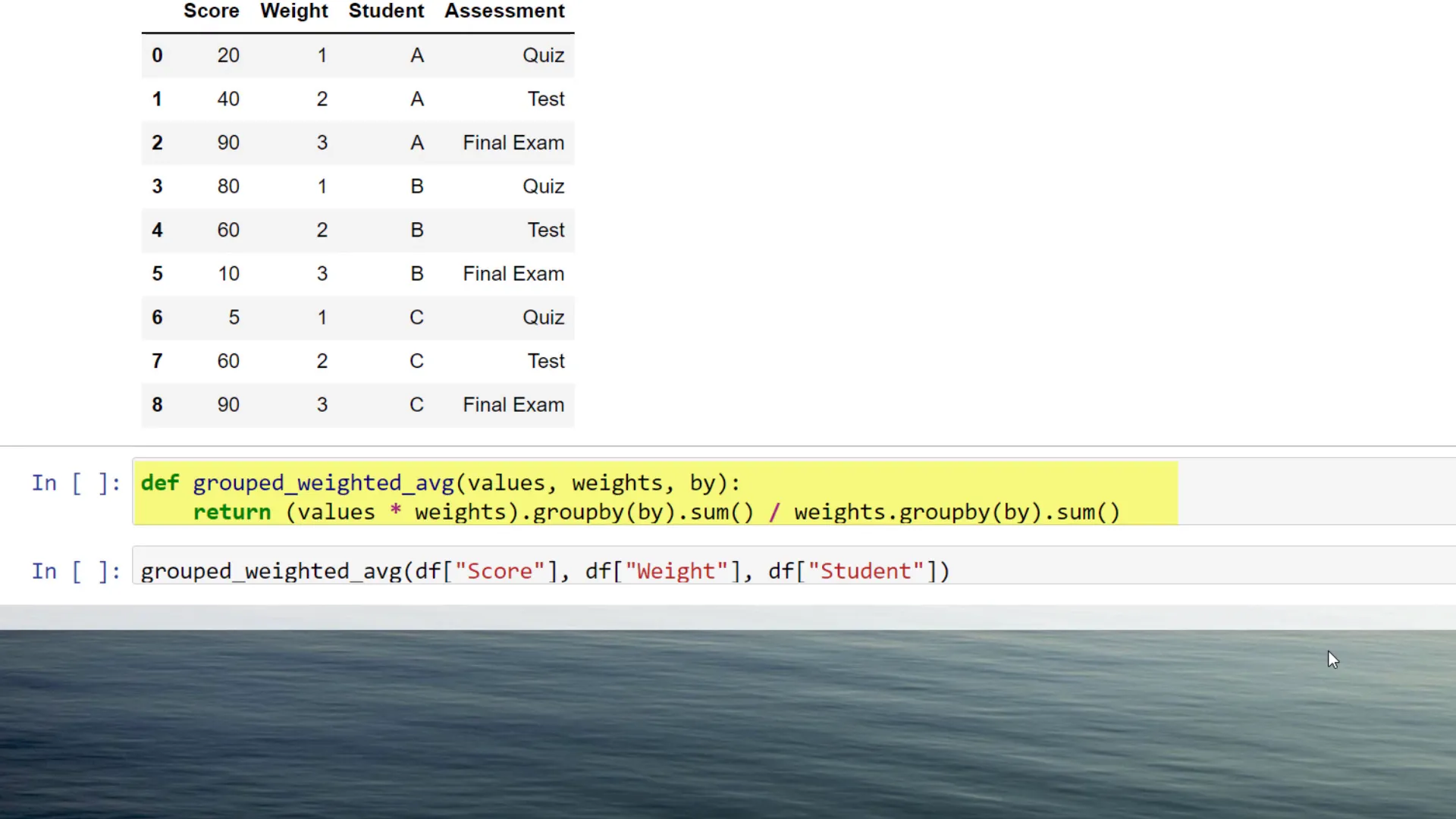
The calculation method remains similar. The only difference is that we will combine it with the groupby method. Here’s how it works:
By executing this line, you will get a new DataFrame containing the weighted average for each student.
Conclusion
In summary, calculating a weighted average in Pandas is a practical way to evaluate scores that carry different weights. By leveraging vectorized calculations and helper functions, you can efficiently manage larger datasets and compute weighted averages for multiple students.


