I Added Google Gemini to Excel… And It Blew My Mind 🤯
Gemini in Excel using VBA: Add AI to Your Spreadsheets (No Coding Required)
Scenario: You have a messy sales sheet and need fast insights, or you want to extract names, translate text, or run formulas with natural language. Instead of exporting data and juggling APIs, bring the model to the place you already work: Excel. This guide shows how to get Gemini in Excel using VBA so you can ask AI questions directly from your workbook.
What this solution does and why it matters
Putting Gemini in Excel using VBA turns Excel into an AI assistant. It sends selected ranges or cell prompts to Gemini, and returns summaries, extracted values, translations, or computed answers right into sheets. You do not need programming skills; the solution is plug and play and supports the latest Gemini models. There is a free Google tier to get started, and an offline alternative if you prefer your data to never leave your machine.
How the integration works at a glance
- Select a range and ask a question, for example, “Analyze my sales, answer in one sentence”.
- Or use the custom Excel formula to run prompts like a normal function.
- Results return into a new worksheet, with a short summary and optional structured outputs.
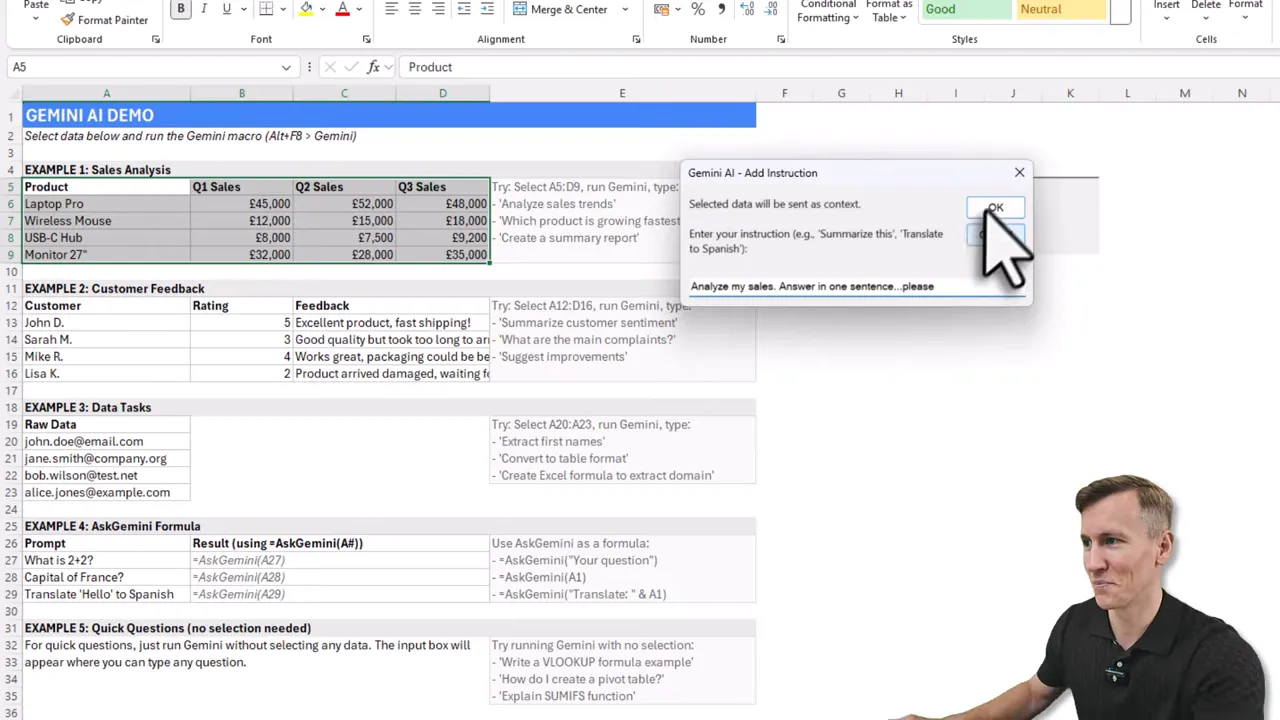
Before you build: simple concepts to understand
There are two moving parts:
- VBA macros inside a macro-enabled workbook to call the Gemini API.
- An API key from Google AI Studio so Excel can authenticate requests.
Step by step setup
1. Download the prepared workbook and source modules
Start by downloading the package from the repository. Extract the zip to a folder and make sure Windows does not block the file in its properties. If you see an unblock option, tick it and apply.
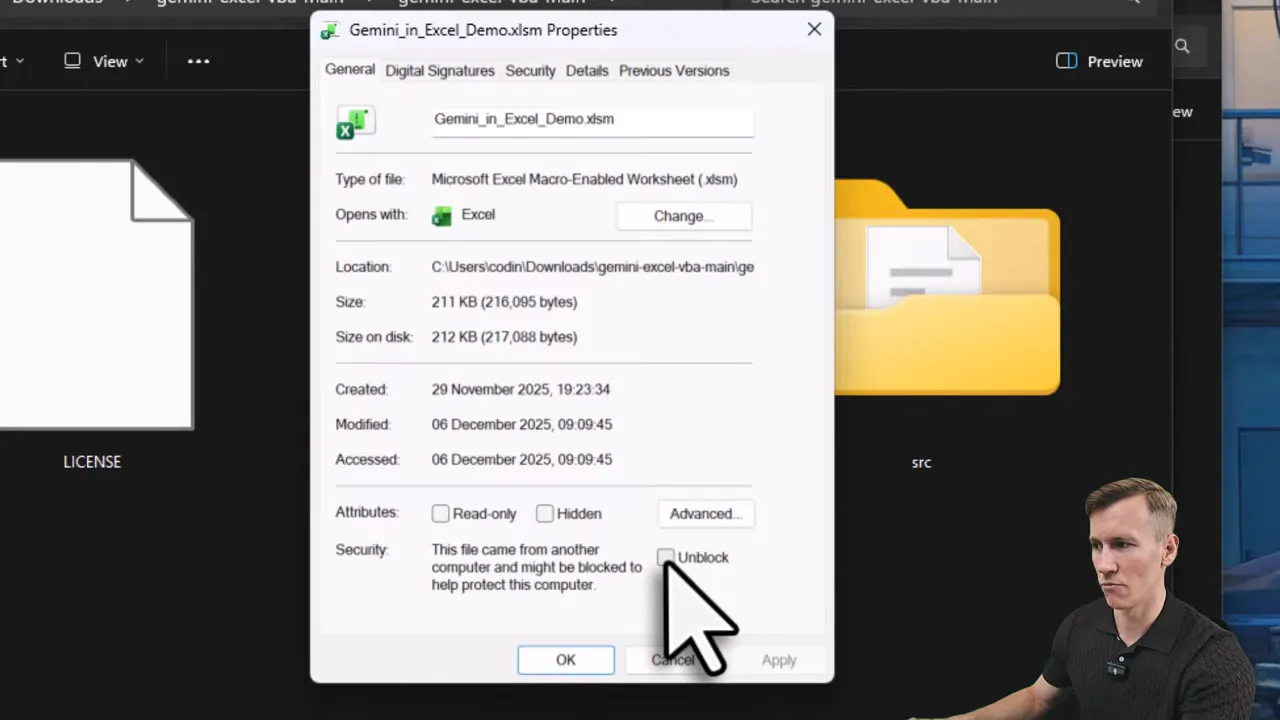
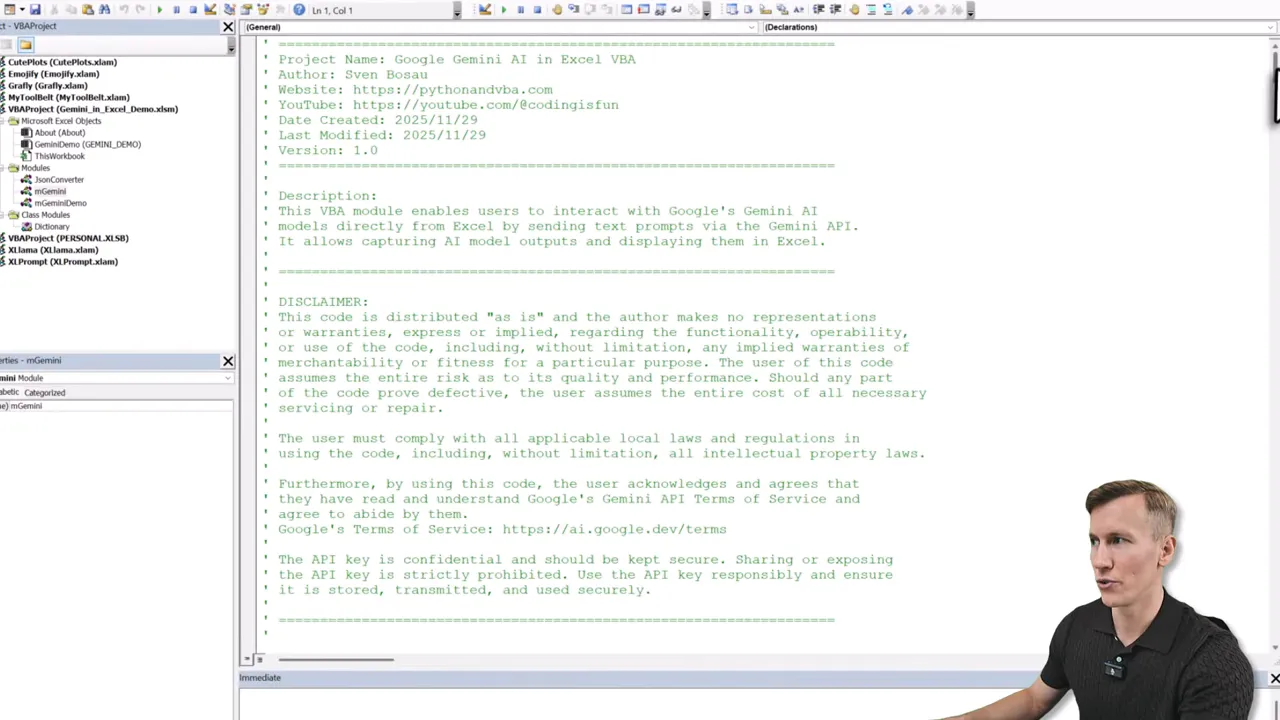
2. Open the macro-enabled workbook and inspect the code
Open the file. It is a Macro Enabled Workbook and contains multiple modules: a JSON converter, the main Gemini module, an optional demo module, and a dictionary class. To view them, enable the Developer tab and open the Visual Basic Editor.
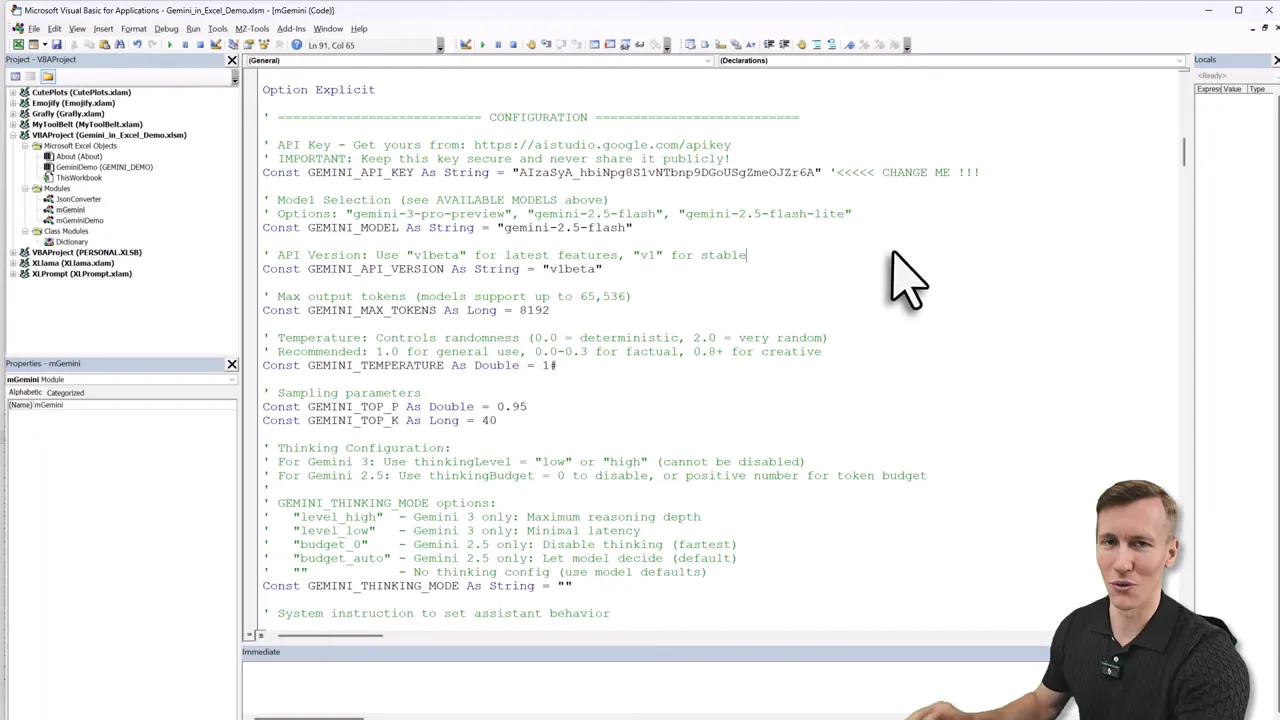
3. Configure the API key
In the configuration section of the Gemini module paste your Google AI Studio API key. Create a key in Google AI Studio, give it a project, then copy and paste it into the VBA config. You can also pick which Gemini model to call, such as Gemini 2.5 or Gemini 3.
4. Test the integration inside Excel
Use the provided button to send a prompt. For example, try a light test like “Tell me an Excel related joke” to confirm everything works and that you get a new sheet with the AI answer.
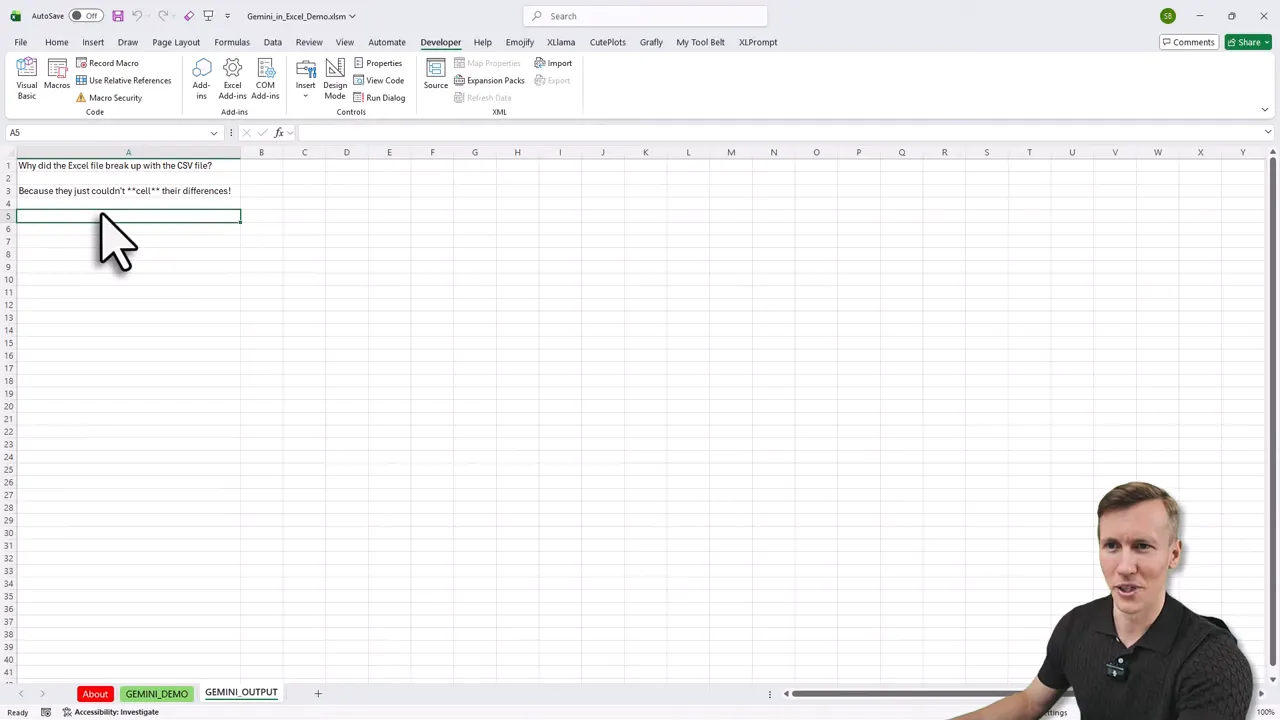
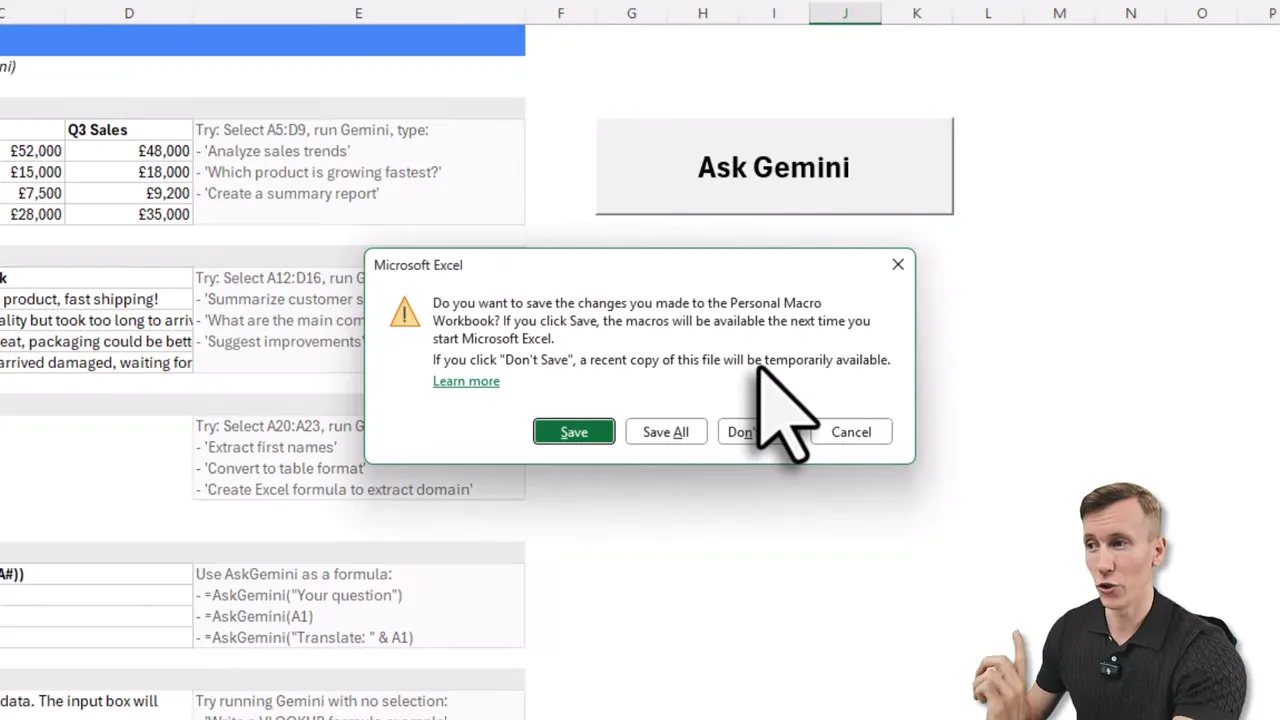
5. Make it available in all workbooks
To run the integration from any workbook, copy the modules into your personal macro workbook (PERSONAL.XLSB). Use the macro recorder to create PERSONAL.XLSB if it is not already present, then drag modules into it from the Visual Basic Editor.
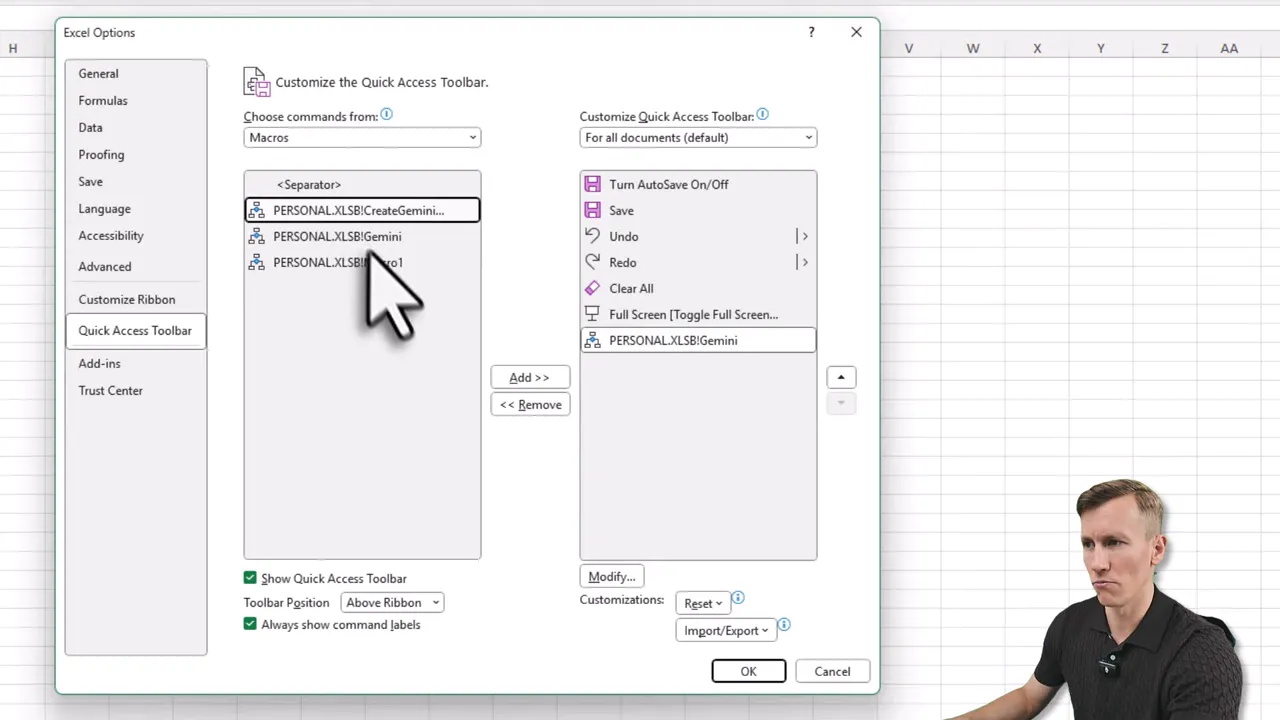
6. Add a Quick Access Toolbar button and use the formula
Add the new macro to the Quick Access Toolbar for one-click access. There is also a custom formula (the R. Gemini formula) that behaves like a normal Excel function. Remember to reference the function in your PERSONAL.XLSB if you see a name error.
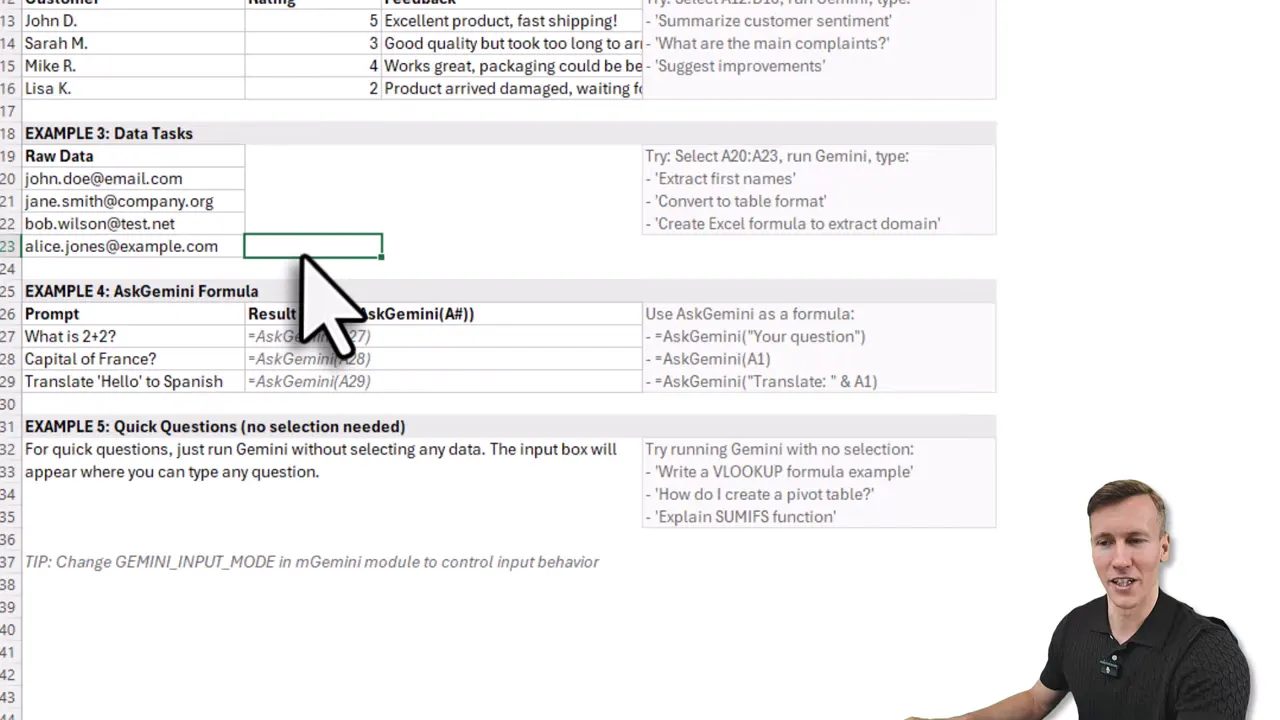
Examples of what you can do
- Sales summary in one sentence from a selected range.
- Extract first names from email addresses with a prompt and return results into a column.
Privacy, cost, and a local alternative
Two important notes:
- Cost: Google offers a free tier, but heavy usage may incur charges. Monitor API usage to avoid surprises.
- Privacy: Sending data to Gemini is not private. Sensitive data will travel to Google servers.
If you want a local, private option, consider XLlama. It is an Excel add-in that runs open source models locally. No API calls, no recurring costs, and your data never leaves your computer. Replace the Gemini formula with the XLlama formula and point it to a local model such as Qwen or Mistral variants. The workflow remains the same: use either range-based prompts or formulas, and results appear in new sheets.
Troubleshooting tips
- If a cell shows a name error for the custom formula, prefix the function with the PERSONAL.XLSB workbook name and an exclamation mark.
- If the workbook does not run macros, confirm that macros are enabled and the file was unblocked in Windows properties.
- Check the API key and the chosen model if responses are missing or return errors.
Why this approach works well
Embedding Gemini in Excel using VBA keeps data in the environment professionals already use for analysis. It reduces context switching, speeds up insights, and makes advanced AI capabilities accessible with minimal friction. For privacy-conscious users, a local model via XLlama provides a strong alternative while preserving the same convenient interface.
Final takeaway
Adding Gemini in Excel using VBA is a practical way to supercharge spreadsheets with AI. The setup is straightforward, the core code is ready to use, and you can choose between cloud convenience and local privacy. Try a simple summary prompt, experiment with the custom formula, and decide which workflow—cloud or local—fits your data needs best. Happy automating! —Sven


